History & Mission

Evolution of IMD-PQS
WHO established the Essential Programme on Immunization (EPI, formerly the Expanded Programme on Immunization) in the late 1970s, creating a need for specialized cold chain equipment that met the demanding performance requirements of low-resource settings. These types of operating environments typically include limited and unreliable fuel and electrical power supplies, as well as challenging climatic conditions. In such environments, equipment must be robust enough to protect valuable and temperature-sensitive vaccine loads. It must also be inexpensive to operate and to maintain. WHO, in consultation with UNICEF Supply Division, therefore drew up the first performance specifications and testing procedures for immunization devices and products.
Products that successfully met the new standards set by WHO and UNICEF were "prequalified" for use in WHO EPI programmes and listed in joint WHO‒UNICEF Supply Division "Product Information Sheets" (PIS), together with information to help national immunization programmes select the most appropriate products for their specific needs.
Over time, WHO expanded the scope of innovative technologies it prequalified to further improve the quality, safety and value-for money of immunization programmes. Through this process of evolution, WHO Immunization Devices, Performance, Quality and Safety (WHO IMD-PQS) was born. In 2000, the PIS paper-based listings were transferred to a globally-accessible, up-to-date electronic format. Product specifications and testing protocols are updated regularly and improved, and the range of products prequalified continues to be extended.
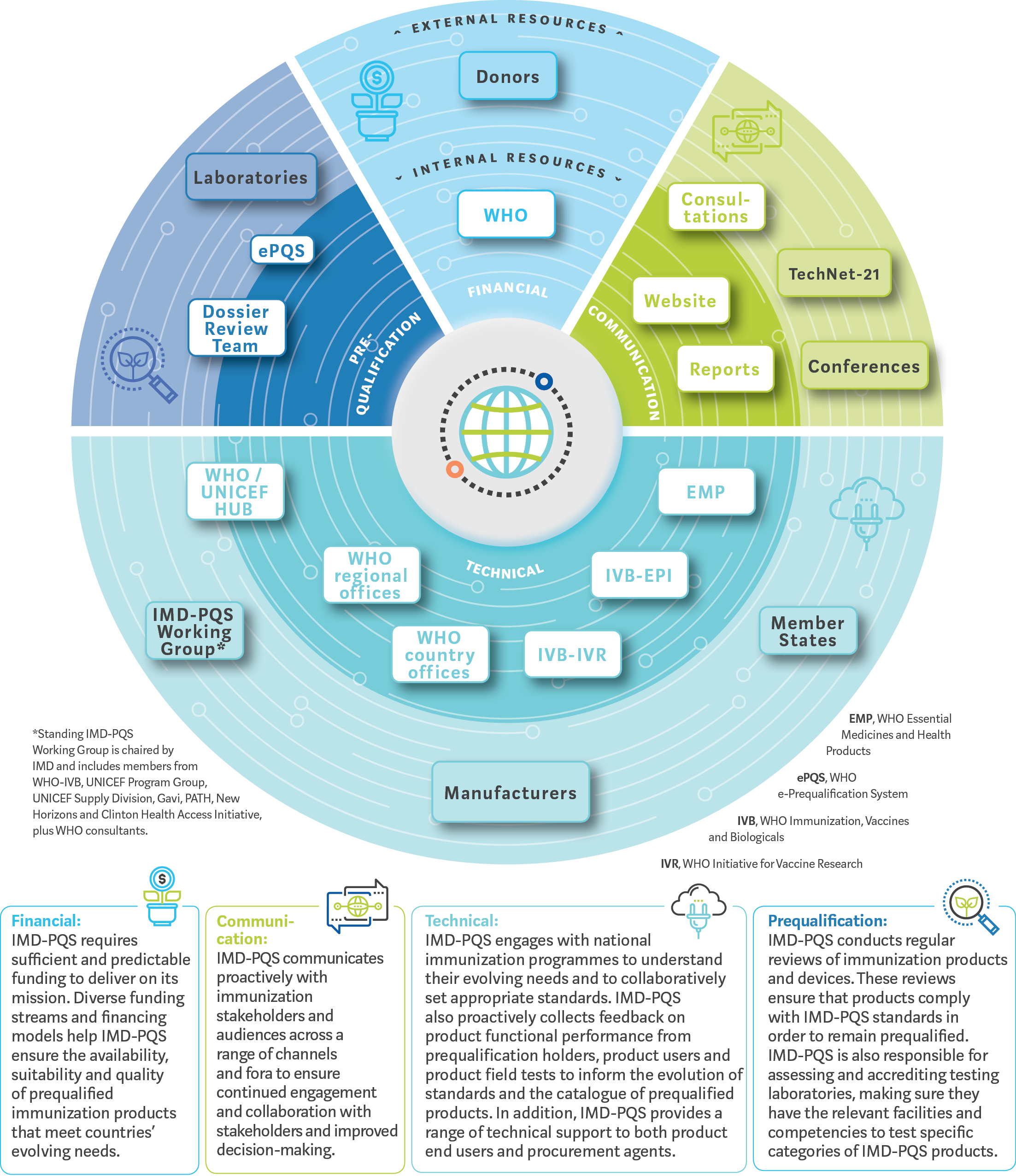
Immunization devices organisational ecosystem
The WHO IMD-PQS initiative is currently managed and coordinated by the Secretariat. The IMD-PQS Secretariat liaises with — and is assisted by — the IMD-PQS Working Group, members of which are representatives of key WHO and UNICEF departments, and immunization technical experts. The Secretariat and the Working Group also engage in dialogue with a range of external experts, including international standards-setting bodies, Prequalification Holders (product manufacturers), ministries of health and other product end users, testing laboratories and a range of specialist agencies.
Additionally, the IMD-PQS Dossier Review panel is a team of experts who assess the dossiers submitted by prospective Prequalification Holders for prequalification.
WHO IMD-PQS: At the core of immunization programmes
Today, WHO prequalification of immunization devices delivers significant value to immunization programmes.
WHO IMD-PQS:
- collects and uses post-market product performance information to help improve technologies and product specifications
- gathers insights about the evolving operating environments of immunization programmes to help industry to meet these needs through product innovation and
- accredits laboratories to test and verify new products and maintain WHO prequalification standards.

Vision and mission
The vision for WHO prequalification of immunization devices is to ensure access to quality, appropriate cold chain products for national immunization programmes worldwide. Its mission is to collaborate closely with EPI programmes, Prequalification Holders, testing laboratories and a range of technical specialist organizations to empower WHO Member States and UN purchasing agencies to procure suitable, reliable products.
Strategy
This mission is achieved by:
- establishing and applying up-to-date norms and product standards of acceptable quality, safety and efficacy
- prequalifying immunization products according to comprehensive evaluation of their quality, safety and efficacy, based on information submitted by the (prospective) Prequalification Holders and inspection of manufacturing sites
- accrediting laboratories to verify that products comply with the relevant specifications and verification protocols
- carrying out post-market monitoring and consultations to help improve technologies and stimulate innovation
- helping to stimulate a healthy and competitive marketplace for immunization products by helping to ensure a fair basis for procurement decisions.