WHO Prequalification - Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Introduction
WHO prequalification (PQ) helps ensure that medical products procured by UN agencies, international procurement or funding agencies, and WHO member states meet acceptable standards of quality, safety and efficacy. It is a significant driver of equity in access to essential medical products.
WHO prequalified health products meet global standards of quality, safety, and efficacy/performance, they optimize use of health resources and improve health outcomes. PQ is designed based on the best international practice combined with assessing aspects of product relevance for low- and medium-income countries (LMIC).
WHO prequalifies:
- immunization devices and cold chain equipment
- In-vitro diagnostics (IVDs) and male circumcision devices (MCDs)
- medicines
- finished pharmaceutical products (FPPs)
- active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
- vaccines
- vector control products.
- Medicines quality control laboratories
Following consultation with stakeholders, WHO developed and implemented key performance indicators (KPIs) in 2017 for its PQ activities. These are important to monitor performance, identify areas for improvement and support accountability by reporting to stakeholders. The KPIs have been aligned for transparent reporting internally and externally to stakeholders.
The KPIs have been implemented in line with the quality management principles of strengthening transparency on PQ processes, activities, and the efficient utilization of resources. The outcome of the monitoring and evaluation reports on these KPIs are used for continuous improvement of PQ processes and activities. The KPIs are based on the high-level overview of the aligned PQ process for different product streams. Figure 1 below shows basic the phases of the PQ process activities, decision points and their key dates.
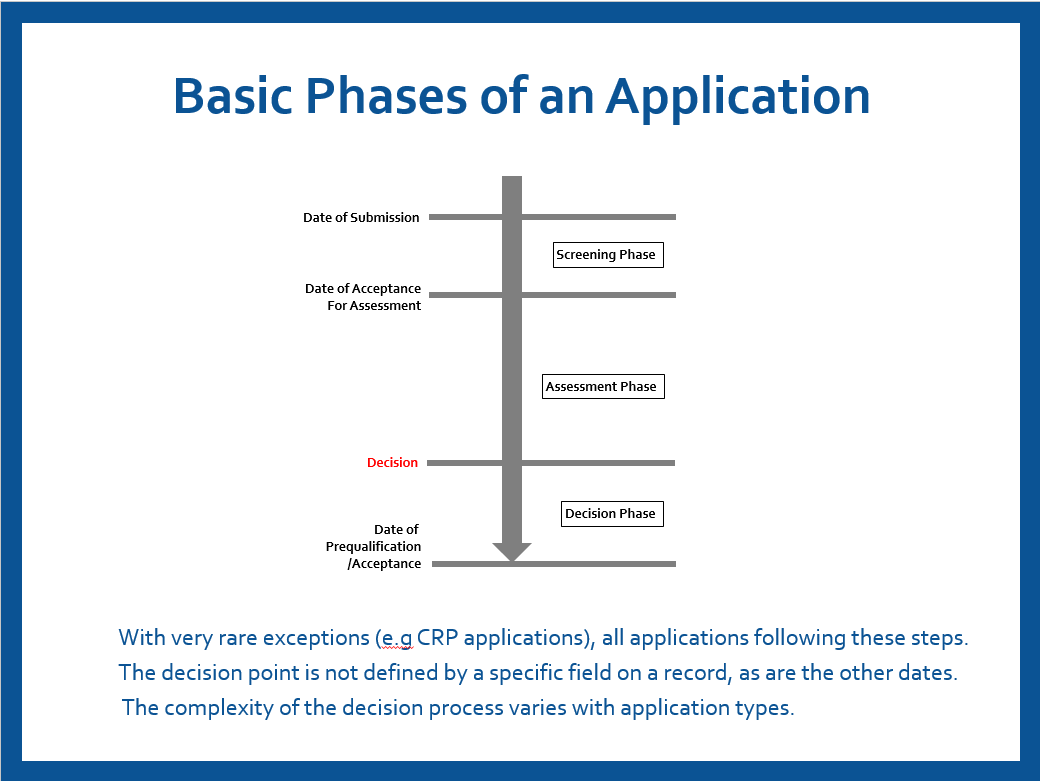
Using figure 1, the determination of the key points and dates for the calculation of the KPIs are based on the following:
- Date of submission: the date when a complete application dossier is submitted by an applicant (manufacturer). In case of rolling submissions, this is the date when the last part of the dossier is submitted by the applicant.
- Screening: reviewing the completeness of the application dossier with respect to specific PQ requirements.
- Date of acceptance for assessment: the date when screening of the submitted application dossier has been completed successfully and can proceed to assessment.
- Assessment phase: this phase includes all assessments to ascertain the product’s quality, safety, and performance, namely:
- assessment of product dossier,
- inspection of manufacturing and clinical testing site(s),
- Independent testing of samples (Vaccines)/performance evaluation of the product (IVDs).
- Decision on assessment: the point and date when the decision is made on latest component of the assessment phase.
- PQ decision: the decision made by WHO to prequalify the product based on the outcomes of all the components of the assessment phase.
- Date of PQ: the date when the product is added to the list of prequalified products.
Maintenance
The KPIs and proposed targets, are reviewed every three (3) years and may be modified following consideration of previous performance, aspirations for continuous improvement, any implementation issues and significant organizational or external changes.
The KPI report, key outputs and achievements for the previous year (January to December) are published on the WHO website within the first quarter of the following year. The KPI results and outputs of the previous year are used to highlight the achievements and inform areas for improvements.