Title
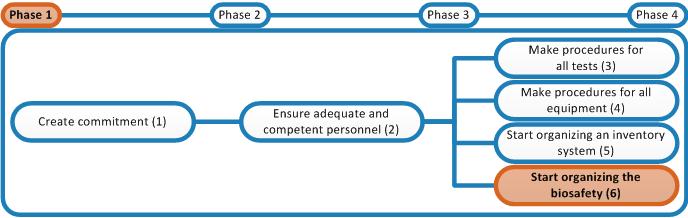
Why
The basis of quality management is: "Write what you do and do what you write". This means that you have to document everything that is routinely done at the laboratory. Hence, every examination and procedure must be documented in Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). SOPs assure that every activity is always done in the same, most optimal way, which decreases chances on errors, accidents and false results. In the case of safety procedures it decreases chances on accidents, infection and spread of pathogens. All the safety procedures of the laboratory must also be documented.
What
A Biosafety Manual must be developed containing all the safety procedures in the laboratory. Safety procedures can be preventive, concurrent and corrective. This means:
- Preventive: Safety precautions and procedures aimed at preventing accidents, laboratory infections, and spread of pathogens.
- Concurrent: In case of accidents, such as a spill or fire, these procedures describe the best way of solving the problem with the least chances on making the accident worse.
- Corrective: When an accident has occurred, these procedures ensure that the root-cause (the primary activity that created the accident) of each accident is found and that actions are taken to prevent the accident from re-occurring.
Everybody must read this Biosafety Manual to know how each procedure should be done correctly. The chapters in the Biosafety Manual will have the outline of Procedure SOPs, hence write the chapters according to the protocol for writing a Procedure SOP in the Master SOP and use the template for a Procedure SOP attached to the Master SOP. An example of a chapter of the biosafety manual is provided in the right-hand column. This is the SOP on Waste Segregation and Disposal provided already earlier in phase 1.
An example list of topics that could be covered by the biosafety manual is provided below. Please note that this is just a list of suggested chapters to give you a headstart. If you think of other topics that should be covered: feel free to include these as well. Remove topics that are not applicable/relevant for the situation in your laboratory.
- Title page
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Responsibilities of the Biosafety Officer
- General Safety Instructions
- Universal Safety Precautions
- Risk Assessment and Scope
- Introduction Checklist (for new employees)
- Annual Communication of Safety Instructions
- Medical Examination and Health Control
- Entry Rules to the Containment Laboratory
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Use of disinfectants
- Specimen Handling and Safety
- Avoiding the Dispersal of Infectious materials
- Use of Pipette and Pipette Aids
- Biological Safety Cabinets
- Fumigation of the biological safety cabinet
- Centrifuge Safety
- Ultraviolet Light Safety
- Electricity Safety
- Compressed Liquefied Gases Safety
- Waste Segregation and Disposal
- Emergency procedure in case of fire
- Procedure in case of spill of infectious material in the laboratory
- Procedure in case of spill of infectious material within the biological safety cabinet
- Emergency procedure in case of major biohazard incident outside the biological safety cabinet
- Risk of Infection in case of Accidents
- Incident Report
How & who
Biosafety Officer:
- Make a list of all the safety procedures that are needed for your laboratory.
- Discuss this list with the Laboratory Manager and staff to determine if it covers all the necessary topics or that topics should be added.
- Once consensus is reached on the outline of the biosafety manual, start writing the chapters. Each chapter is a safety procedure which is in essence an SOP, hence, follow the protocol for writing a Procedure SOP in the Master SOP and use the template for a Procedure SOP attached to the Master SOP. See the example biosafety manual chapter provided in the right-hand column.
- Let the Laboratory Manager and one other senior staff member review the procedures you've developed.
- Correct the procedures based on comments of the two reviewers.
- Sign the procedures after completion and let the two reviewers also sign.
- All the procedures together form the Biosafety Manual. Present the Biosafety Manual to all the staff members and explain the use of it.
Laboratory manager:
- Discuss the list of topics that should be covered by the biosafety manual (developed by the Biosafety Officer) with the Biosafety Officer and other staff members to determine if it is complete.
- Review biosafety procedures within a reasonable time-frame when the Biosafety Officer asks for this. Make sure that another (senior) staff member also reviews the procedures.
- Include all the procedures in the Read and Understand List when completed and authorized.
- Present each procedure in a weekly staff meeting to all staff members. Indicate that everybody has to read the procedures and sign the Read and Understand List after reading.
- When new staff members are hired, let them read the Biosafety Manual before they start working in the laboratory.