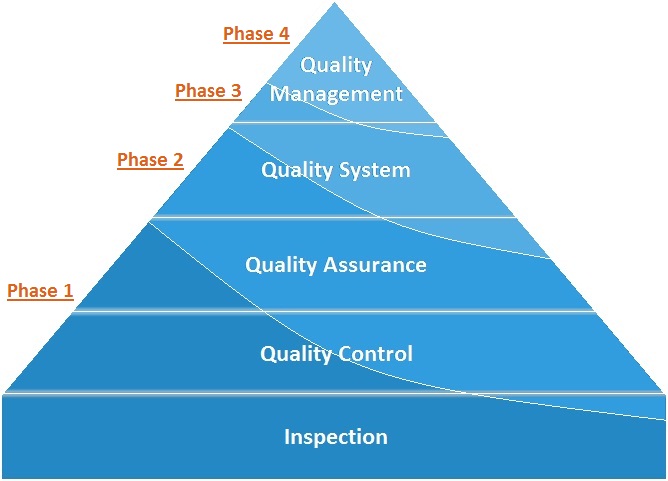
Focus of the Phases of the LQSI Tool
To give a logical structure to the process of implementing the quality management system the stepwise plan was divided over four phases of implementation, which each phase having a specific focus. The tool is constructed such that, even when a laboratory does not reach full implementation of the quality management system, it has already improved its quality service provision from phase 1, and as such has benefited already.
- Phase 1: Ensuring that the primary process of the laboratory operates correctly and safely
- Phase 2: Controlling and assuring quality and creating traceability
- Phase 3: Ensuring proper management, leadership and organization
- Phase 4: Create continuous improvement and prepare for accreditation
Phase 1
Phase 1 focuses on implementing the absolute basic elements that all laboratory should have in place regardless of size or location. Without these elements it is impossible to guarantee adequate and safe services. The primary process of the laboratory is the core process of laboratory testing, from the pre-analytical stage (the sample is collected, received at the laboratory, registered and processed) via the analytical stage (the actual laboratory test is performed and the result is recorded) to the post-analytical stage (the result reported and archived and the sample is discarded/archived).
Practically the major activities of phase 1 include:
- Formation of a quality project team
- Upgrading background knowledge of quality management amongst staff and management
- Development of Standard Operating Procedures for laboratory tests and equipment to assure that testing is performed in a standardized way, according to a defined methodology and with adequate adherence to safety rules
- Establishment of an equipment maintenance system
- Upgrading laboratory biosafety with appointment of a biosafety officer, biosafety training to all staff, biosafety assessment and introduction of a biosafety manual
Phase 2
Whereas in phase 1 the absolute essentials necessary to enable safe and adequate laboratory practice are established, phase 2 focuses on the basic fundaments of the quality management system: quality control and quality assurance. Quality control mechanisms, among which proficiency testing, are implemented in the complete primary process of the laboratory. Also the next dimension of the quality management system: quality assurance is implemented with establishment of:
- An adequate stock and ordering system in which incoming supplies are checked for compliance with quality requirements
- A document control system and information management system to create traceability of laboratory information
- Standard Operating Procedures for all processes performed in the laboratory
Phase 3
Quality is a systems approach. This means that it is not limited to merely implementing controls, procedures and forms, but it also affects the management and structure of the organization. In phase 1 and 2 the fundaments quality control and quality assurance were established. To get the most out of these fundaments, they must start to function in a system. For this proper organization, management and leadership are needed which will be implemented in phase 3. Practically the major activities are:
- Setting up a policy cycle based on a proper vision and mission that feed into the planning of the laboratory. With management review and drafting of new plans based on the outcomes the policy cycle is closed
- Documenting the quality management system: development of a quality manual
- Setting up an internal audit system
- Validation of examination procedures
Phase 4
The philosophy of a quality management system according to ISO 15189 rests on the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle as developed by Edward Deming. Not only measures are implemented to assure quality but the organization must also learn from the mistakes made and use these to continually improve the work. In phase 4 systems are implemented that enables passive and active identifications of points for improvement and use these to optimize quality services. This phase ends with placing the dots on the i, so that the laboratory is ready to apply for accreditation.
Major activities are:
- Establishment of a complaint handling system
- Establishment of a nonconformity management system
- Validation of equipment
- Failure mode and effect analysis for risk management
- Continuous competency improvement of staff: establishment of a continuing education programme and performance appraisal
- Organizing an external (mock) audit to identify and resolve the remaining non compliances with ISO 15189