أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
Background
[INFOxNRI1]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[BGxINT]
المعلومات الأساسية
تسعى مدونة المنظمة العالمية لقواعد الممارسة بشأن توظيف العاملين الصحيين على المستوى الدولي ("المدونة") التي اعتُمدت في عام 2010 في جمعية الصحة العالمية الثالثة والستين (قرار جمعية الصحة العالمية 63-16)، إلى تعزيز فهم توظيف العاملين الصحيين الدوليين وإدارته إدارة أخلاقية بتحسين البيانات والمعلومات والتعاون الدولي.
وتحثّ المادة 7 من المدونة الدول الأعضاء في المنظمة على تبادل المعلومات عن توظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي. ويُكلّف المدير العام للمنظمة بتقديم تقرير بهذا الشأن إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية كل ثلاث سنوات.
وقد أكملت الدول الأعضاء في المنظمة الجولة الرابعة من الإبلاغ الوطني في أيار/ مايو 2022. وقدم المدير العام للمنظمة تقريراً عن التقدم المُحرز في التنفيذ إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية الخامسة والسبعين في أيار/ مايو 2022 (ج75/14). وسلط التقرير المتعلق بالجولة الرابعة الضوء على ضرورة تقييم الآثار المترتبة على هجرة العاملين الصحيين في سياق مواطن الضعف الزائدة الناجمة عن جائحة كوفيد-19. ولهذا الغرض، اجتمع من جديد فريق الخبراء الاستشاري المعني بمدى ملاءمة المدونة وفعّاليتها (ج73/9). وبناءً على توصيات فريق الخبراء الاستشاري، نشرت الأمانة قائمة المنظمة لدعم وضمانات القوى العاملة الصحية لعام 2023.
وتتمثل أداة الإبلاغ الوطني في أداة للتقييم القُطري الذاتي لتبادل المعلومات ورصد المدونة. وتمكّن أداة الإبلاغ الوطني من جمع وتبادل البينات والمعلومات الحالية حول توظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي. وسوف تُعرض نتائج الجولة الخامسة من الإبلاغ الوطني على المجلس التنفيذي (في دورته السادسة والخمسين بعد المائة) في كانون الثاني/ يناير 2025 في إطار التحضير لجمعية الصحة العالمية الثامنة والسبعين.
الموعد النهائي لتسليم التقارير هو 31 آب/ أغسطس 2024.
تنص المادة 9 من المدونة على تكليف المدير العام للمنظمة بتقديم تقارير دورية إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية عن استعراض مدى فعّالية المدونة في تحقيق أهدافها المعلنة والاقتراحات المتعلقة بتحسينها. وسيجتمع فريق استشاري من الخبراء بقيادة الدول الأعضاء في عام 2024، لإجراء الاستعراض الثالث للمدونة. وسيقدم التقرير للاستعراض إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية الثامنة والسبعين.
ولطرح أي استفسارات أو طلب التوضيحات حول ملء الاستبيان الإلكتروني، يُرجى الاتصال بنا على العنوان التالي: WHOGlobalCode@who.int.
ما هي مدونة المنظمة العالمية لقواعد الممارسة؟
بيان إخلاء المسؤولية: سوف تُتاح البيانات والمعلومات التي تُجمع باستخدام أداة الإبلاغ الوطني للاطلاع العام عن طريق قاعدة بيانات أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (https://www.who.int/teams/health-workforce/migration/practice/reports-database) في أعقاب مداولات جمعية الصحة العالمية الثامنة والسبعين. وسوف تُستخدم البيانات الكمية لتزويد بوابة بيانات حسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية بالبيانات (http://www.apps.who.int/nhwaportal/).
تسعى مدونة المنظمة العالمية لقواعد الممارسة بشأن توظيف العاملين الصحيين على المستوى الدولي ("المدونة") التي اعتُمدت في عام 2010 في جمعية الصحة العالمية الثالثة والستين (قرار جمعية الصحة العالمية 63-16)، إلى تعزيز فهم توظيف العاملين الصحيين الدوليين وإدارته إدارة أخلاقية بتحسين البيانات والمعلومات والتعاون الدولي.
وتحثّ المادة 7 من المدونة الدول الأعضاء في المنظمة على تبادل المعلومات عن توظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي. ويُكلّف المدير العام للمنظمة بتقديم تقرير بهذا الشأن إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية كل ثلاث سنوات.
وقد أكملت الدول الأعضاء في المنظمة الجولة الرابعة من الإبلاغ الوطني في أيار/ مايو 2022. وقدم المدير العام للمنظمة تقريراً عن التقدم المُحرز في التنفيذ إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية الخامسة والسبعين في أيار/ مايو 2022 (ج75/14). وسلط التقرير المتعلق بالجولة الرابعة الضوء على ضرورة تقييم الآثار المترتبة على هجرة العاملين الصحيين في سياق مواطن الضعف الزائدة الناجمة عن جائحة كوفيد-19. ولهذا الغرض، اجتمع من جديد فريق الخبراء الاستشاري المعني بمدى ملاءمة المدونة وفعّاليتها (ج73/9). وبناءً على توصيات فريق الخبراء الاستشاري، نشرت الأمانة قائمة المنظمة لدعم وضمانات القوى العاملة الصحية لعام 2023.
وتتمثل أداة الإبلاغ الوطني في أداة للتقييم القُطري الذاتي لتبادل المعلومات ورصد المدونة. وتمكّن أداة الإبلاغ الوطني من جمع وتبادل البينات والمعلومات الحالية حول توظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي. وسوف تُعرض نتائج الجولة الخامسة من الإبلاغ الوطني على المجلس التنفيذي (في دورته السادسة والخمسين بعد المائة) في كانون الثاني/ يناير 2025 في إطار التحضير لجمعية الصحة العالمية الثامنة والسبعين.
الموعد النهائي لتسليم التقارير هو 31 آب/ أغسطس 2024.
تنص المادة 9 من المدونة على تكليف المدير العام للمنظمة بتقديم تقارير دورية إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية عن استعراض مدى فعّالية المدونة في تحقيق أهدافها المعلنة والاقتراحات المتعلقة بتحسينها. وسيجتمع فريق استشاري من الخبراء بقيادة الدول الأعضاء في عام 2024، لإجراء الاستعراض الثالث للمدونة. وسيقدم التقرير للاستعراض إلى جمعية الصحة العالمية الثامنة والسبعين.
ولطرح أي استفسارات أو طلب التوضيحات حول ملء الاستبيان الإلكتروني، يُرجى الاتصال بنا على العنوان التالي: WHOGlobalCode@who.int.
ما هي مدونة المنظمة العالمية لقواعد الممارسة؟
بيان إخلاء المسؤولية: سوف تُتاح البيانات والمعلومات التي تُجمع باستخدام أداة الإبلاغ الوطني للاطلاع العام عن طريق قاعدة بيانات أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (https://www.who.int/teams/health-workforce/migration/practice/reports-database) في أعقاب مداولات جمعية الصحة العالمية الثامنة والسبعين. وسوف تُستخدم البيانات الكمية لتزويد بوابة بيانات حسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية بالبيانات (http://www.apps.who.int/nhwaportal/).
Disclaimer
[INFOxNRI2]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[disclaim]
بيان إخلاء المسؤولية
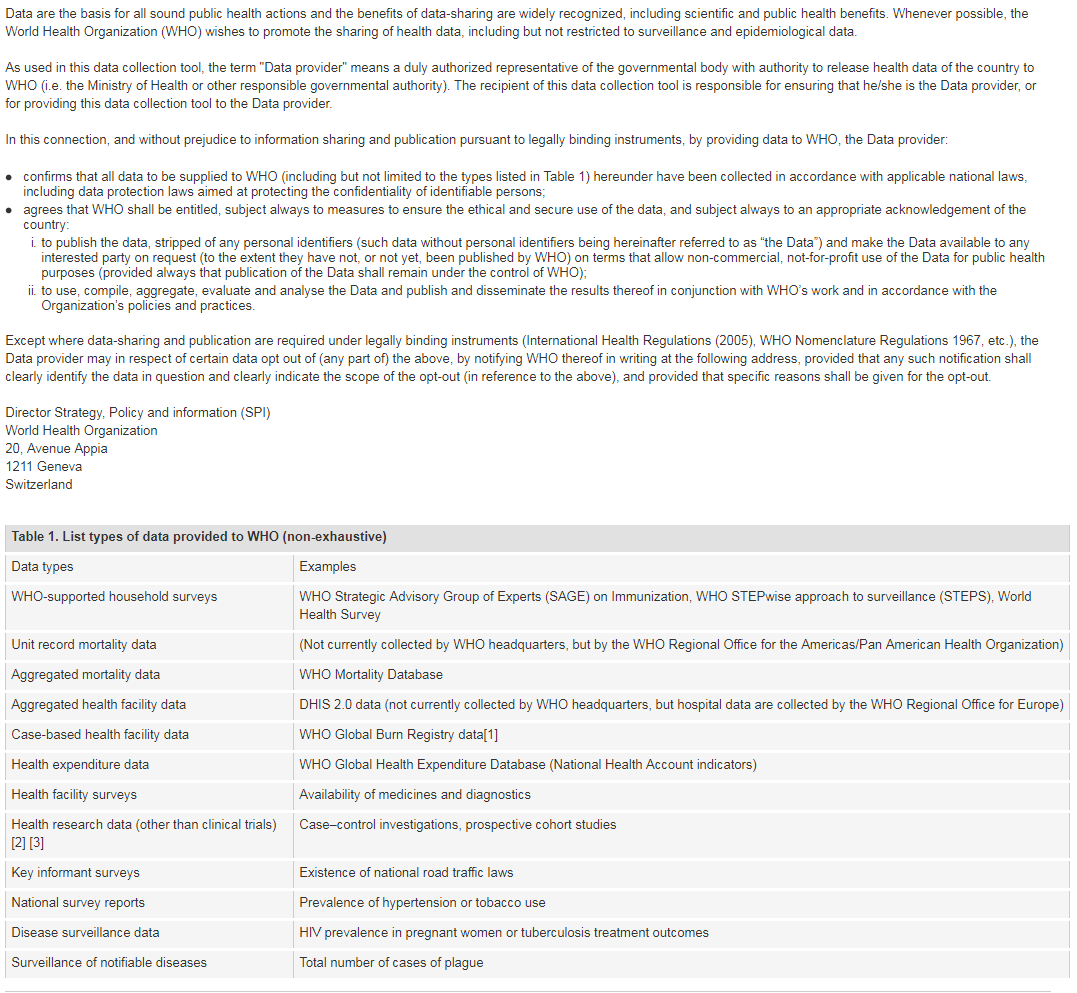
[1] Note: Case-based facility data collection as that in the WHO Global Bum Registry does not require WHO Member State approval.
[2] The world health report 2013: research for universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013 (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85761/2/9789240690837_eng.pdf)
[3] WHO statement on public disclosure of clinical trial results: Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015 (http://www.who.int/ictrp/results/en/, accessed 21 February 2018).
For more information on WHO Data Policy kindly refer to http://www.who.int/publishing/datapolicy/en/

[1] Note: Case-based facility data collection as that in the WHO Global Bum Registry does not require WHO Member State approval.
[2] The world health report 2013: research for universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013 (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85761/2/9789240690837_eng.pdf)
[3] WHO statement on public disclosure of clinical trial results: Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015 (http://www.who.int/ictrp/results/en/, accessed 21 February 2018).
For more information on WHO Data Policy kindly refer to http://www.who.int/publishing/datapolicy/en/
لقد قرأت وفهمت سياسة منظمة الصحة العالمية بشأن استخدام ومشاركة البيانات التي جمعتها المنظمة في الدول الأعضاء خارج سياق طوارئ الصحة العامة
Contact Details
[INFOxNRI3]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[CI]
الاتصال تفاصيل
اسم الدولة العضو:
Lithuania
اسم المسؤول الوطني المُعيَّن
State Accreditation Service for Health Care Activities
منصب المسؤول الوطني المُعيَّن
Division of Specialist Activities
المؤسسة التي ينتمي إليها المسؤول الوطني المُعيَّن
State Accreditation Authority for Health Care under the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Lithuania
البريد الإلكتروني:
riginao@who.int,agne.raukstiene@vaspvt.gov.lt,vaspvt@vaspvt.gov.lt,WHOGlobalCode@who.int
رقم الهاتف:
+370 653 06363
Contemporary issues
[INFOxNRI4]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[NRIxI]
تُعد الأسئلة المميزة بعلامة * إلزامية. ولن يسمح النظام بالتسليم إذا لم يُرد على جميع الأسئلة الإلزامية.
[INFOx1]
المشكلات الحالية المتعلقة بهجرة العاملين الصحيين وتنقلهم
[Q1x1]
هل كانت مشكلة توظيف العاملين الصحيين على المستوى الدولي مصدر قلق لبلدك، في السنوات الثلاث الماضية؟
لا، ليست هذه مشكلة في بلدي
[Q1x2]
هل كانت مشكلة الاعتماد الدولي على العاملين الصحيين (التوظيف الدولي للعاملين الصحيين لتلبية الاحتياجات المحلية) مصدر قلق لبلدك، في السنوات الثلاث الماضية؟
لا، ليست هذه مشكلة في بلدي
Health Personnel Education
[INFOxNRI5]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx2]
تعليم العاملين الصحيين وتوظيفهم واستدامة النظام الصحي
[Q2]
هل يتخذ بلدك تدابير لتعليم وتوظيف واستبقاء القوة العاملة في مجالي الصحة والرعاية التي تلائم الظروف الخاصة ببلدك، بما في ذلك في المجالات التي تشتد فيها الحاجة؟
نعم
[Q2x1]
يُرجى وضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه :
2.1 التدابير المتخذة لضمان استدامة القوى العاملة في مجالي الصحة والرعاية
2.2 التدابير المُتخذة لمعالجة سوء التوزيع الجغرافي واستبقاء العاملين في مجالي الصحة والرعاية*
2.3 التدابير الأخرى ذات الصلة بشأن تعليم وتوظيف واستبقاء القوى العاملة في مجالي الصحة والرعاية وفق ما يتناسب مع الظروف الخاصة لبلدك
[Q2x1x1]
2.1.1 التدابير المتخذة لضمان استدامة القوى العاملة في مجالي الصحة والرعاية
التنبؤ بالاحتياجات المستقبلية من القوى العاملة في مجال الصحة والرعاية لتوجيه التخطيط
The Ministry of Health has developed an action plan for the years 2024-2029 aimed at reducing the uneven distribution of healthcare professionals nationwide and addressing shortages of certain professional qualifications and specializations in the healthcare sector. The action plan outlines the following measures: 1. Monitoring of Healthcare Workforce: Implementation of systems to track and monitor the shortage, training, distribution, and recruitment of healthcare professionals. 2. Improvement of Forecasting and Planning: Enhancements in forecasting and planning for healthcare workforce needs. 3. Empowerment, Recruitment, and Retention: Strategies to empower, attract, and retain healthcare professionals. It is planned to prepare an overview of the current situation of health human resources management in Lithuania, analyze best practices from foreign countries, and provide recommendations for human resources management, demand forecasting, inclusion, retention, improvement, and more. Based on these documents, a long-term health human resources management strategy (up to 2030) would be developed and approved at the national level.
مواءمة تعليم القوى العاملة المحلية في مجالي الصحة والرعاية مع احتياجات النظام الصحي
Planned Investments in Training and Professional Development. A budget of 30.7 million euros has been allocated for healthcare professionals recruitment measures from the 2021-2027 European Union funds investment program. These funds will be directed towards: • Enhancing Human Resources Management Efficiency: Improving the efficiency of healthcare human resources management. • Financing Study Costs: Covering the costs of healthcare education. • Empowerment, Recruitment, and Retention Models: Developing and implementing models for the empowerment, recruitment, and retention of healthcare professionals within healthcare institutions. • Increasing Prestige and Professional Orientation: Elevating the prestige and professional orientation of the most critically needed professional qualifications and specializations. • Other Related Initiatives: Additional measures to support the overall recruitment and retention strategy.
تحسين جودة التعليم والعاملين الصحيين بما يتماشى مع احتياجات تقديم الخدمات
Ensuring high-quality healthcare services can only be achieved by adequately trained and educated high-level healthcare professionals. To enhance the quality of residency studies and residency bases across the country, the Ministry of Health will allocate funding for the acquisition and improvement of educational competencies of physician residents' mentors – 344,000 euros have been earmarked for this purpose. On July 31, 2024, Order No. V-788 was issued, titled „Order on the approval of the procedure for updating the educational competencies of the resident physician supervisor and acquiring and updating the educational competencies of the resident physician mentor. “ A project funded by the European Union's 2021–2027 investment program is dedicated to physician resident mentors who will work in healthcare institutions outside the largest cities of Lithuania, including regional areas. The project's goal is to provide these mentors with educational skills to ensure a quality learning process and a positive psycho-emotional climate for physician residents in their residency bases. Additionally, it aims to help young doctors integrate more easily and effectively into the healthcare system. Approved professional development programs are designed for healthcare professionals and administrative staff working in personal healthcare institutions. These programs focus on developing both general (management, leadership, communication, emotional literacy, etc.) and specialized competencies. Based on the Long-Term Care Service Provision Model Development Project Plan, which was approved by the Government in December 2021, a plan for the training, retraining, and professional development of long-term care specialists is to be prepared. A legal act aimed at improving the qualifications and working conditions of healthcare professionals is planned to be drafted. This act will regulate the financing mechanism for the professional development of healthcare professionals, introducing a professional qualification development fund for healthcare professionals, financed by the state, institutions, organizations, and personal funds.
خلق فرص العمل التي تتماشى مع الاحتياجات الصحية للسكان
Aiming to address the shortage of healthcare professionals in Lithuania's national health system, the Ministry of Health has requested personal healthcare institutions to provide information on their preliminary capabilities to cover the tuition fees of pupils, students, and resident doctors, in accordance with the order of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Lithuania No. V-1080, dated November 7, 2008. Additionally, institutions were asked to provide information on other possible incentive measures for attracting healthcare professionals. The Ministry of Health has compiled lists of incentive measures to present comprehensive information, allowing pupils, students, and resident doctors to find all relevant information in one place and make informed decisions regarding contract agreements with personal healthcare institutions. This list will aid in attracting healthcare professionals with the most needed qualifications to personal healthcare institutions experiencing the greatest shortage of these specialists. These healthcare professionals could contribute to the provision of quality and timely healthcare services, addressing the health needs of the population. Starting from July 1, 2024, a patient transportation service will be launched in Lithuania. Patients who meet the transportation criteria will be able to order the service by calling 1808, from home to the healthcare facility and back. The expansion of this service will bring healthcare services closer to patients and thus help the most vulnerable populations (due to health, poverty, age). The aim of this measure is to ensure that age, level of participation, health status, or other factors do not hinder access to necessary healthcare services.
إدارة توظيف العاملين الصحيين على المستوى الدولي
Lithuania adheres to the principles of the World Health Organization (WHO) Global Code of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel, aiming to ensure ethical and responsible international recruitment of health care professionals. This Code aims to strengthen health systems in developing countries and maintain a balance between the migration of health care professionals and the needs of national health systems. Adherence to Ethical Principles Compliance with the Code: Lithuania is committed to adhering to the WHO Global Code, which sets out ethical principles for the international recruitment of health care professionals, aiming to protect the health systems of developing countries from brain drain. Development of National Strategies Formulating National Policies: The Ministry of Health (SAM) develops national strategies that include measures for the recruitment, training, and retention of health care professionals to ensure that those working in Lithuania meet the country's needs and international standards. International Collaboration Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements: Lithuania collaborates with other countries to ensure fair and responsible recruitment of health care professionals, sharing best practices and information on migration trends. Incentive Programs Incentive Programs: Lithuania implements various incentive measures to retain and attract health care professionals, such as financial support for students, residents, and doctors who commit to working in the country's health care facilities for a specified period. Return Programs Return and Reintegration Programs: Lithuania encourages emigrated health care professionals to return by offering reintegration programs, including professional development, job placements, and financial support. Education and Awareness Information Dissemination: The Ministry of Health and other relevant institutions conduct information campaigns to inform health care professionals about international recruitment rules, opportunities, and responsibilities, as well as the principles of the WHO Code. Challenges and Solutions Shortage of Specialists in Certain Areas Targeted Measures: To address the shortage of specialists, Lithuania implements targeted measures such as financial incentives, professional development programs, and improvements in infrastructure in regional health care facilities. Impact of Migration on the Health System Ensuring Balance: Lithuania strives to maintain a balance between international recruitment of specialists and the needs of the national health system, considering the specifics and priorities of the country's health care sector. Lithuania actively implements measures to ensure responsible international recruitment of health care professionals in accordance with the WHO Global Code of Practice. These measures help strengthen the country's health care system, ensure the sustainability of health care professionals, and contribute to improving public health.
تحسين إدارة العاملين الصحيين
The Ministry of Health plans to develop and approve professional qualification enhancement programs for healthcare professionals and administrative staff working in personal health care institutions. These programs will focus on both general (management, leadership, communication, emotional intelligence, etc.) and specific competencies. Training sessions are scheduled to commence from 2024 and continue through 2029. An allocation of €1.8 million from the 2021–2027 European Union funds investment program has been designated for this measure. The planned qualification enhancement will focus on primary care, specialized fields (including emergency and urgent medical care, mental health services), long-term care, and pharmacy. It will also include the requalification of emergency medical specialists. To improve the monitoring and planning of healthcare professionals' qualifications, the development of an IT tool—the Healthcare Professionals Competency Platform—is planned.
وضع أحكام محددة بشأن تنظيم العاملين الصحيين وتوظيفهم أثناء الطوارئ
Plans are underway for the development and modernization of top-level infectious disease cluster centers and regional infectious disease cluster centers, with an emphasis on improving infectious disease management. Two top-level centers are set to be established for the modernization of emergency medical departments in regional hospitals to ensure effective patient flow management and accessibility and quality of emergency medical services during epidemics/pandemics. A systematic strengthening of the health system's resilience to operate in emergencies is planned, with an allocation of €148 million (excluding VAT) for infrastructure development and equipment acquisition. This initiative aims to ensure regional-level infectious disease treatment capacities during crises (at least 650 beds) and create conditions for conducting research on dangerous and highly dangerous infections, integrating into international scientific programs. The goal is to adapt the emergency medical departments and intensive care units of major national hospitals to effectively provide emergency medical services to a large number of patients simultaneously in the event of high and very high-risk incidents, ensuring safe working conditions for staff working under hazardous conditions. Plans are underway to develop legislation aimed at enhancing the preparedness of healthcare institutions for operating in emergencies. The following actions are planned under the modernization action plan for healthcare institutions' collaboration and infrastructure adaptation for emergencies: Requirements Specification: Establish requirements that healthcare institutions must meet to ensure their preparedness for emergencies. Legal Foundations: Create legal frameworks to support healthcare institutions and their personnel in preparing for and operating during emergencies. Resource Cooperation: Develop legal provisions to facilitate more effective cooperation of resources (material and human). From the 2021-2027 EU funds investment program, it is planned to acquire additional vehicles to meet increased demand due to a higher number of emergency medical service stations and the need to transport patients to specialized centers in acute conditions. This includes updating some vehicles due to wear and tear. On January 18, 2024, an Expert Working Group was established to review healthcare professional education programs and to incorporate competencies necessary for preparedness for emergencies and wartime threats into these programs. The tasks of the Expert Working Group are: To identify the competencies required by healthcare sector professionals to provide rapid and coordinated healthcare services during emergencies or wartime (hereinafter referred to as "competencies"). To establish a strategy for the development of these competencies.
أُخرى
In all cases, the professional qualification of doctors, nurses, dentists, oral care specialists and other regulated professions health care specialists acquired outside the Republic of Lithuania must be recognized in accordance with the Directive 2005/36/EC. Practice shows that the recognition of professional qualification of a medical doctor is recognized by practically all applicants. Problems arise with professional qualification of specialists from third countries, because the duration of studies is often significantly shorter than in Lithuania. During the recognition, the work experience is also assessed. High length of practise sometimes compensates for the shorter duration of studies. Recognition of professional qualifications is only one part of procedure to legally provide personal health care services in Lithuania. Once the professional qualification is recognized, specialist must obtain their license. In order to obtain a license, the conditions for proficiency in the Lithuanian language and permission to temporarily live and work in Lithuania are needed, which often causes problems for individuals.
[Q2x2x1]
ضع علامة على كل ما ينطبق ل التدابير المُتخذة لمعالجة سوء التوزيع الجغرافي واستبقاء العاملين في مجالي الصحة والرعاية
2.2.1 التعليم
2.2.2 التنظيم
2.2.3 الحوافز
2.2.4 الدعم
[Q2x2x1x1]
2.2.1.1 التعليم التدابير
المؤسسات التعليمية في المناطق الريفية/ الناقصة الخدمات
Educational institutions (universities, colleges, and vocational training schools/centers) are in the major cities of the country.
قبول الطلاب من المناطق والمجتمعات الريفية / الناقصة الخدمات
Admissions to educational institutions are carried out according to the general procedure established by the institutions. This procedure allows individuals from rural or underserved areas to apply and be admitted to educational institutions.
المنح الدراسية والإعانات التعليمية المقدمة
المواضيع/ المناهج ذات الصلة في برامج التعليم و/أو التطوير المهني
(إعادة) توجيه برامج التعليم نحو الرعاية الصحية الأولية
أُخرى
[Q2x2x2x1]
2.2.2.1 التنظيم التدابير
المنح الدراسية وإعانات التعليم مع اتفاقات إعادة الخدمات
According to the Order No. V-1080 of November 7, 2008, by the Minister of Health of the Republic of Lithuania, students, trainees, or medical residents can benefit from a legal framework that regulates financial support from municipal administrations or healthcare institutions. This support is available to those studying in non-state-funded places. By entering into study financing agreements, they are required to fulfill contractual obligations by working for a specified number of years in the healthcare institution, thus contributing to the needed healthcare workforce.
اتفاقات الخدمة الإلزامية مع العاملين الصحيين التي لا تتعلق بالمنح الدراسية أو إعانات التعليم
تعزيز نطاق الممارسة للعاملين الصحيين الحاليين
Requalification of Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Specialists Starting January 1, 2024, the new regulations for providing Emergency Medical Services (EMS) will come into effect. According to these regulations, EMS drivers will be required to hold a paramedic professional qualification. This change aims to enhance the capabilities of EMS teams, ensuring that all members, including drivers, are equipped with the necessary medical knowledge and skills to effectively respond to emergencies. Pharmacy Specialist Training To better utilize the potential of pharmacists as competent health care specialists, additional training for pharmacy professionals is planned. This training will focus on expanding the range of patient-centered pharmaceutical care services and advanced practice pharmacy roles. Specifically, the following initiatives are planned: 1. Development of Additional Services: By the second half of 2022, a phased implementation of new services provided by pharmacists will begin. This will continue through to 2030, with new regulations defining these services and their delivery conditions. 2. Competency Requirements: Regulations will outline the competencies required for pharmacists, specifying the necessary training hours, procedures, target patient groups, and collaboration with physicians. 3. Enhanced Pharmaceutical Care: The new services will include comprehensive pharmaceutical care and extended practice roles, which will aim to improve patient outcomes through better medication management and health advice. These measures are intended to strengthen the role of pharmacists in the healthcare system, ensuring that they can provide high-quality, patient-focused services and work effectively within the healthcare team.
تبادل المهام بين المهن المختلفة
Family Doctor Team Model Comprehensive Family Doctor Team: To improve service quality and accessibility, family medicine services are provided by a comprehensive family doctor team. This team includes a family doctor, nurses, midwife, nurse assistant, physiotherapist, lifestyle medicine specialist, and case manager. Competency Distribution: Functions of team members are allocated according to their expanded competencies, thereby more effectively utilizing the specialists' skills. Retraining of Emergency Medical Services Specialists Paramedic Qualification: From January 1, 2024, following the new Emergency Medical Services provision requirements, emergency medical drivers must have a paramedic professional qualification. Retraining Programs: Training and professional development courses are organized to ensure that emergency medical services specialists are adequately prepared for emergencies. Development of Pharmacy Specialists' Competencies Pharmaceutical Care and Advanced Practice Services: To better utilize pharmacists' potential, additional patient-oriented pharmaceutical care and advanced practice pharmacist (pharmacist-healthcare specialist) services are being developed. Regulation and Training: From the second half of 2022 to 2030, it is planned to gradually regulate additional services provided in pharmacies and their conditions, including the enhancement of pharmacists' competencies. Retraining and Professional Development of Specialists Integrated Health Care Services: Continuous training is organized to improve the competencies of health care specialists, providing new knowledge and practical skills for working with innovative and advanced technologies. Retraining for Internal Medicine and Pediatric Doctors: There are plans to allow internal medicine and pediatric doctors to additionally obtain family doctor qualifications. Practical Implementation Examples Competency Platform Health Care Specialist Competency Platform: An IT tool is planned to be created to monitor and plan the professional development and practical skills acquisition processes of health care specialists. Regional Initiatives Strengthening Regional Health Care Centers: Projects are being carried out in regional health care centers to strengthen the composition and competencies of specialist teams, thereby ensuring better service accessibility.
أحكام بشأن المسارات للدخول في الممارسات الجديدة أو المتخصّصة بعد الخدمة في الريف
The Ministry of Health has initiated changes to the Regulations for the Implementation and Supervision of Medical Residency and Dental Residency Programs, as approved by the Government's decree. The changes, effective from January 1, 2023, include extending the duration of certain residency programs and introducing a minimum requirement for professional practice. Specifically, by 2027, at least 35% of medical residents' professional practice must be completed outside university hospitals. To qualify as a residency base, healthcare institutions now only need to have a medical resident mentor (a new role) responsible for overseeing the acquisition of practical skills by medical residents, replacing the previous requirement for a medical resident supervisor. Funds from the initiative will be used to train doctors who wish to become medical resident mentors. Additionally, the Ministry of Health is implementing an EU-funded project titled "Recruiting Specialists to Reduce Health Disparities" (Project No. 08.4.2-ESFA-V-617), with a budget of €668,800. This project aims to fund residency training for doctors (at least 34 individuals) who commit to working for a minimum of 2 years in healthcare facilities in specific districts, as stipulated in their agreements.
أُخرى
[Q2x2x3x1]
2.2.3.1 الحوافز التدابير
رد النفقات المالية الأخرى
Additional Salary Supplements: Health professionals working in regions or specialties with significant shortages may receive additional salary supplements. These supplements aim to make positions in underserved or high-need areas more attractive. Retention Bonuses: Financial bonuses are offered to healthcare workers who commit to staying in their positions for an extended period, particularly in areas with high demand or difficult working conditions. Financial Support for Education and Training Study Funding: Financial support is provided to cover the costs of education for students pursuing degrees in health-related fields. This can include scholarships or loans that are partially forgiven if the recipient works in designated underserved areas. Training and Certification Costs: Funds are allocated to cover the costs of professional development and certification for existing health care professionals. This includes costs associated with additional qualifications, specialized training, and continuing education. Support for Recruitment and Retention Relocation Assistance: Financial aid is provided to healthcare professionals who relocate to work in high-need areas. This can include relocation expenses, housing allowances, and other support to ease the transition. Employment Grants: Grants or subsidies are offered to health care institutions to support the hiring of additional staff. These funds can help offset the costs associated with expanding services or increasing staff numbers. Incentives for Mentorship and Supervision Mentorship Stipends: Financial incentives are offered to experienced professionals who take on mentorship roles, particularly in training new specialists or supervising their work. This aims to encourage experienced professionals to share their knowledge and support the development of new talent. Supervision Allowances: Additional funding is provided to institutions that facilitate supervision and support for new or less experienced health care professionals. Bonuses for Extra Duties and Responsibilities Performance-Based Bonuses: Health professionals who take on additional duties or responsibilities beyond their standard roles may receive performance-based bonuses. This includes taking on extra shifts, working in challenging conditions, or providing additional services. Specialty Bonuses: Additional financial incentives are given to professionals who acquire specialized skills or work in high-demand specialties, such as emergency medicine, psychiatry, or geriatrics. Implementation and Monitoring Evaluation and Adjustments: The effectiveness of these financial measures is regularly evaluated to ensure they meet their goals of addressing shortages and improving workforce retention. Adjustments are made based on feedback from health professionals and performance data. Transparency and Communication: Clear communication about available financial support and eligibility criteria is essential to ensure that health professionals are aware of the incentives and can access them effectively.
فرص التعليم
To ensure the occupancy of state-funded study places and to enhance the prestige of certain professional qualifications, as well as to encourage professional orientation and shift public perceptions about specific healthcare professions, the following communication activities are planned: 1. Sharing Professional Experience: Healthcare professionals (preferably from the same cities) will visit schools and high schools to share their professional experiences and career paths. 2. Encouragement Events: Events, practical assignments, and tours of healthcare institutions will be organized to motivate students to choose healthcare professions, providing them with a clearer understanding of the benefits and challenges of these careers. 3. Information Dissemination for Medical Students: Dissemination of information among medical students in integrated studies, guiding them to choose the most needed qualifications after six years of study, such as family medicine, emergency medicine, geriatrics, and psychiatry. 4. Information Dissemination for Nursing Students: Information dissemination and incentives will be targeted at general practice nursing students to better inform them about their career options and opportunities in the healthcare sector. These activities aim to shift societal attitudes towards healthcare professions and encourage young people to pursue careers in this field.
فرص التقدم الوظيفي أو النمو المهني
To enhance the competencies of healthcare professionals and other specialists in the healthcare field and ensure continuous professional development, the goal is to provide new knowledge and improve practical skills. This includes integrating advanced healthcare services and working with innovative, cutting-edge technologies. From the 2014-2020 EU funding period and the 2014-2021 European Economic Area Financial Mechanism "Health" program, various projects were implemented to enhance specialists' qualifications. However, due to the ongoing need for continuous improvement to enhance service quality, qualifications development and retraining activities will continue into the 2022-2030 period. Experiences from pandemic management encourage the exploration of solutions to strengthen primary healthcare, expand telemedicine and mobile service options (such as remote consultations, patient monitoring, home visits by family doctors, emotional support, health maintenance advice, etc.). Advances in health technology and the precision of diagnostic and treatment methods are altering the roles of various professions in the treatment process and presenting new challenges for ensuring the safety and quality of health services. This involves planning, evaluating, maintaining, and improving the competencies of healthcare professionals to meet medical standards and creating favorable conditions for implementing innovative healthcare service delivery models. In restructuring the network of healthcare institutions, the aim is to ensure that primary care services within the scope of family medicine are provided exclusively by a fully-fledged family medicine team. This team would include a family doctor, nurses, a midwife, a nursing assistant, a physiotherapist, a lifestyle medicine specialist, and a case manager. The functions of team members should be allocated based on their developed competencies to enhance service quality and accessibility through more effective use of specialist skills. For a fully integrated family medicine team, it is essential to ensure not only a complete composition of required specialists but also the redistribution of their responsibilities, ongoing qualification improvement/retraining (e.g., internal medicine and pediatric specialists could acquire additional qualifications in family medicine), adaptation of existing service delivery methodologies, algorithms, and recommendations, as well as the development and implementation of new ones.
التقدير المهني
التقدير الاجتماعي
Public Visibility: The activities of healthcare professionals are often highlighted through media, social networks, and other communication channels. This helps the public learn about their achievements and contributions to the healthcare system. Awards and Recognition Ceremonies: Awards ceremonies are held to honor healthcare professionals who have achieved significant results or contributed to important projects. These awards may be given by the state, municipalities, or professional associations. Patient Feedback: Patient reviews and gratitude letters are also considered important aspects of social recognition. Many healthcare professionals receive positive feedback from patients who value their work and commitment. Professional Organization Recognition: Professional organizations and associations evaluate and acknowledge the contributions and achievements of specialists, granting them certificates, titles, or other recognition markers. Educational and Public Awareness Activities Profession Promotion in Schools and Universities: Events, seminars, and practical tasks are organized in schools and universities where professionals share their experiences with young people. This helps improve the image of the profession and encourages youth to choose a career in healthcare. Public Awareness Campaigns: Organizations and institutions run campaigns to increase public understanding of the work and importance of healthcare professionals. This may include advertising campaigns, social media posts, informational posters, and more. Documentation of Professional Achievements Professional Achievements Documentation: Healthcare professionals can be recognized for their achievements, such as scientific research, innovations, or exceptional services. These achievements can be published in scientific journals, healthcare magazines, or other sources. Social Responsibility Projects: Involvement in social responsibility projects, such as free health screenings, educational programs, or assistance to socially vulnerable groups, also contributes to social recognition. Participation in International Projects International Projects and Collaboration: Participation in international healthcare projects and collaboration with foreign professionals provides opportunities for international recognition and experience, which can enhance social recognition at the national level. Career and Professional Development Career Opportunities: Various career development and professional growth opportunities are provided, including leadership positions, teaching, and mentoring roles, which help professionals gain recognition for their contributions and experience in the healthcare system.
فرص الحصول على الإقامة الدائمة و/ أو الجنسية للعاملين الصحيين الدوليين
أُخرى
[Q2x2x4x1]
2.2.4.1 الدعم التدابير
ظروف العمل اللائقة والمأمونة
Health and Safety Regulations Occupational Health and Safety Standards: Lithuania adheres to strict occupational health and safety regulations that apply to all workplaces, including healthcare facilities. These regulations ensure that healthcare professionals work in environments that minimize risks and protect their health. Regular Safety Inspections: Healthcare facilities undergo regular safety inspections to ensure compliance with health and safety standards. This includes checking for proper sanitation, ergonomic workplace design, and adequate safety equipment. Workplace Safety Training Mandatory Training Programs: Healthcare professionals are required to undergo regular training in workplace safety, including emergency procedures, infection control, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Continuing Education: Ongoing education programs are provided to keep healthcare workers informed about the latest safety protocols, technological advancements, and best practices. Supportive Work Environment Ergonomic Workspaces: Facilities are designed to be ergonomic, reducing physical strain and preventing injuries. This includes adjustable furniture, proper lighting, and equipment designed to minimize physical effort. Mental Health Support: Recognizing the high stress associated with healthcare professions, mental health support and counseling services are available to help professionals manage stress and prevent burnout. Infection Control Measures Infection Prevention Protocols: Healthcare settings are equipped with rigorous infection control protocols to protect staff from exposure to harmful pathogens. This includes regular disinfection of surfaces, proper waste management, and protocols for handling infectious materials. Vaccination Programs: Vaccination programs are in place to protect healthcare professionals from infectious diseases. These programs are regularly updated based on current health threats. Fair Compensation and Benefits Competitive Salaries: Efforts are made to ensure that salaries for healthcare professionals are competitive and reflect the high level of responsibility and expertise required. Additional Benefits: Healthcare professionals receive additional benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, and retirement plans, contributing to their overall job satisfaction and security. Work-Life Balance Flexible Scheduling: Initiatives to improve work-life balance include flexible scheduling options and support for part-time work or job-sharing arrangements. Leave Policies: Generous leave policies, including sick leave, parental leave, and vacation time, are in place to help professionals manage their personal and family responsibilities. Emergency Preparedness Preparedness Plans: Healthcare facilities have emergency preparedness plans in place for dealing with crises such as natural disasters, pandemics, or mass casualty events. These plans are regularly reviewed and updated. Crisis Training: Regular crisis management training ensures that healthcare professionals are prepared to handle emergencies effectively and safely. Legal Protections Legal Framework: Lithuanian labor laws provide protections for healthcare professionals, including regulations on working hours, breaks, and conditions of employment. Reporting Mechanisms: There are established mechanisms for reporting unsafe working conditions or occupational hazards, ensuring that concerns are addressed promptly and effectively.
ظروف المعيشة اللائقة والمأمونة
فرص التعلم عن بعد/ التعلم الإلكتروني
أُخرى
[Q3x1]
هل هناك سياسات و/أو قوانين محددة توجّه توظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي وإدماج العاملين الصحيين المدربين في الخارج في بلدك؟
لا
[Q3x2]
هل هناك أي سياسات و/أو أحكام في بلدك بشأن خدمات الرعاية الصحية الدولية المقدمة عن بعد عن طريق العاملين الصحيين المقيمين في الخارج؟
لا
[Q3x3]
هل أنشأ بلدك قاعدة بيانات أو سن مجموعة من القوانين واللوائح المتعلقة بتوظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي، والمعلومات المتعلقة بتنفيذها، حسب الاقتضاء؟
لا
[Q4]
اعترافاً بدور الجهات الحكومية الأخرى، هل وضعت وزارة الصحة آليات (مثل السياسات والعمليات والوحدات) للرصد والتنسيق على نطاق القطاعات بشأن المسائل المتعلقة بتوظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي؟
لا
[Q5]
يُرجى توضيح الخطوات التي اتخذها بلدكم لتنفيذ التوصيات التالية للمدونة:
ضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه:
ضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه:
5.1 اتُخذت تدابير أو يجري النظر فيها لإدخال تغييرات على القوانين أو السياسات المتعلقة بالعاملين الصحيين وفقاً لتوصيات المدونة.
On July 31, 2024, Order No. V-788 was issued, titled “Order on the approval of the procedure for updating the educational competencies of the resident physician supervisor and acquiring and updating the educational competencies of the resident physician mentor.”
5.2 اتخذت إجراءات للاتصال وتبادل المعلومات على نطاق القطاعات بشأن توظيف الموظفين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي، وللتعريف بالمدونة، في الوزارات والإدارات والوكالات المعنيّة على المستويين الوطني و/أو دون الوطني.
On July 5, 2024, at the national and / or regional level, a letter titled “Request to provide information and conduct active communication“ was sent to healthcare institutions. The purpose was to gather information on all agreements established and terminated by healthcare institutions and/or municipalities regarding the employment of specialists under contractual obligations. Additionally, the letter requested information on the incentive measures implemented by healthcare institutions to attract health specialists, as well as details regarding vacant positions for healthcare specialists.
5.3 اتُخذت تدابير للتشاور مع أصحاب المصلحة في عمليات صنع القرار و/أو إشراكهم في الأنشطة المتعلقة بتوظيف العاملين الصحيين على المستوى الدولي.
See the previous information provided in section 5.2
5.4 تُحفظ السجلات في جميع وكالات التوظيف الخاصة بشأن العاملين الصحيين الذين تسمح لهم السلطات المختصّة بالعمل في نطاق ولايتها.
5.5 تُشجّع الممارسات الجيدة، على نحو ما تدعو إليه المدونة، وتُعزّز ويُروَّج لها على نطاق وكالات التوظيف الخاصة.
5.5 أ الترويج للمدونة على نطاق وكالات التوظيف الخاصة.
5.5 ب التشريعات أو السياسات المحلية التي تتطلب الممارسة الأخلاقية من قِبل وكالات التوظيف الخاصة، بما يتماشى مع مبادئ المدونة وموادها.
5.5 ج الإشهاد العام أو الخاص على الممارسات الأخلاقية لوكالات التوظيف الخاصة.
5.5 د أُخرى
5.6 لا شيء مما ذكر أعلاه
Government Agreements
[INFOxNRI6]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx3]
الاتفاقات بين الحكومات بشأن هجرة العاملين الصحيين أو تنقلهم
[Q6]
هل أبرم بلدك أو حكومتك دون الوطنية أي اتفاقات و/أو وضع ترتيبات ثنائية أو متعددة الأطراف أو إقليمية تتعلق بتوظيف و/أو تنقل العاملين الصحيين على الصعيد الدولي؟
لا
Responsibilities, rights and recruitment practices
[INFOxNRI9]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx4]
المسؤوليات والحقوق وممارسات التوظيف
[Q7]
إذا كان بلدك يوظف/ يستضيف موظفين صحيين دوليين للعمل في قطاعي الصحة والرعاية، ما هي الضمانات القانونية و/أو الآليات الأخرى التي أُنشئت للعاملين الصحيين المهاجرين وضمان تمتعهم بالحقوق والمسؤوليات القانونية نفسها التي تتمتع بها القوى العاملة الصحية المدربة محلياً؟
يُرجى وضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه:
يُرجى وضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه:
يُعيَّن الموظفون الصحيون المهاجرون باستخدام آليات تسمح لهم بتقييم الفوائد والمخاطر المرتبطة بالوظائف واتخاذ قرارات ملائمة التوقيت ومستنيرة بشأن التوظيف.
يُعيَّن الموظفون الصحيون المهاجرون ويرقّون وتُحدّد أجورهم بالاستناد إلى معايير موضوعية مثل مستوى المؤهلات وسنوات الخبرة ودرجة المسؤولية المهنية على قدم المساواة مع القوى العاملة الصحية المدربة محلياً.
The same conditions and requirements are applied as for Lithuanian health care specialists
يتمتع العاملون الصحيون المهاجرون بالفرص نفسها التي تتمتع بها القوى العاملة الصحية المدربة محلياً لتعزيز تعليمهم المهني ومؤهلاتهم وتقدمهم الوظيفي.
The same conditions and requirements are applied as for Lithuanian health care specialists
توجد ترتيبات مؤسسية لضمان الهجرة الآمنة/ التنقل الآمن وإدماج العاملين الصحيين المهاجرين.
وُضعت تدابير لتشجيع الهجرة الدائرية للعاملين الصحيين الدوليين
تدابير أخرى (بما في ذلك التدابير القانونية والإدارية) لضمان ممارسات استقدام الموظفين والتوظيف العادلة للعاملين الصحيين المدربين في الخارج و/أو المهاجرين (يُرجى ذكر التفاصيل).
لا توجد تدابير مطبقة
لا ينطبق – لا يستضيف/ يوظف البلد عاملين صحيين أجانب
[Q8]
إذا كان العاملون الصحيون من بلدك يعملون في الخارج في قطاعي الصحة والرعاية، يُرجى تقديم معلومات عن التدابير التي اتُخذت أو التي يُعتزم اتخاذها في بلدك لضمان استقدامهم وتوظيفهم على نحو عادل؛ وهجرتهم هجرة آمنة؛ وعودتهم؛ والاستعانة بالمغتربين في بلدك، والصعوبات التي تواجه في هذا الصدد.
يُرجى وضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه:
يُرجى وضع علامة على كل الخيارات التي تنطبق في القائمة الواردة أدناه:
الترتيبات الخاصة بالتوظيف العادل
الترتيبات الخاصة بعقود العمل اللائق وظروف العمل اللائقة في بلدان المقصد
الترتيبات الخاصة بالتنقل الآمن
الترتيبات الخاصة بالعودة وإعادة الإدماج في سوق العمالة الصحية في بلدك
التدابير الخاصة بإشراك المغتربين لدعم النظام الصحي في بلدك
أُخرى
لا توجد تدابير مطبقة
The same conditions and requirements are applied as for Lithuanian health care specialists
لا ينطبق – العاملون الصحيون من بلدي لا يعملون في الخارج
International migration
[INFOxNRI10]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx5]
مسارات الهجرة الدولية والتنقل الدولي للعاملين الصحيين
[Q9x1]
9.1 إذا كان بلدك يستضيف العاملين الصحيين الدوليين للعمل في قطاعي الصحة والرعاية، كيف يأتون إلى بلدك؟ (ضع علامة على كل ما ينطبق)
| طلب (فردي) مباشر للتعليم أو التوظيف أو التجارة أو الهجرة أو الدخول إلى البلد | اتفاقات بين الحكومات تسمح بتنقل العاملين الصحيين | تيسير عملية التوظيف من قِبل وكالات التوظيف الخاصة أو أصحاب العمل | خدمات استشارية خاصة بشأن التعليم/ الهجرة لتيسير التنقل | مسارات أخرى (يُرجى التحديد) | ما هو المسار الأكثر استخداماً؟ يُرجى إدراج البيانات الكمية إن وُجدت. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| أطباء | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| ممرضون | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| قابلات | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| أطباء أسنان | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| صيادلة | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
[Q9x1oth]
[Q9x2]
9.2 إذا كان العاملون الصحيون من بلدك يعملون/ يدرسون في الخارج، كيف يغادرون بلدك؟ (ضع علامة على كل ما ينطبق)
| طلب (فردي) مباشر للتعليم أو التوظيف أو التجارة أو الهجرة أو الدخول إلى بلد المقصد | اتفاقات بين الحكومات تسمح بتنقل العاملين الصحيين | اتفاقات بين الحكومات تسمح بتنقل العاملين الصحيين | اتفاقات بين الحكومات تسمح بتنقل العاملين الصحيين | مسارات أخرى (يُرجى التحديد) | ما هو المسار الأكثر استخداماً؟ يُرجى إدراج البيانات الكمية إن وُجدت | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| أطباء | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| ممرضون | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| قابلات | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| أطباء أسنان | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| صيادلة | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| مهن أخرى | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
[Q9x2oth]
Recruitment & migration
[INFOxNRI11]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx6]
البيانات الخاصة بتوظيف العاملين الصحيين الدوليين وهجرتهم
يُعد تحسين توافر البيانات وإمكانية مقارنتها دولياً ضرورياً لفهم الديناميكية العالمية لهجرة العاملين الصحيين ومعالجتها. يُرجى استشارة مسؤول الاتصال المعني بحسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية في بلدك، إن وجد، للتأكد من أن البيانات الواردة أدناه تتسق مع تقارير حسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية.*
(للاطلاع على التفاصيل الخاصة بمسؤول الاتصال المعني بحسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية في بلدك، يُرجى الرجوع إلى النسخة الإلكترونية من أداة الإبلاغ الوطني أو الاتصال على عنوان البريد الإلكتروني التالي:WHOGlobalCode@who.int)
[Q10]
هل توجد في بلدك أي آلية (آليات) أو كيان (كيانات) تُعنى بالاحتفاظ بالسجلات الإحصائية الخاصة بالعاملين الصحيين المولودين في الخارج والمدربين في الخارج؟
نعم
[Q10x1]
أين تُحفظ هذه السجلات؟ (ضع علامة على كل ما ينطبق)
سجلات التوظيف أو تصاريح العمل
قاعدة بيانات العاملين في وزارة الصحة
سجل العاملين الصحيين المصرّح لهم بمزاولة المهنة
أُخرى
[Q10x2]
هل يتضمن السجل بيانات مصنفة حسب نوع الجنس عن الموظفين الصحيين المولودين في الخارج و/أو المدربين في الخارج؟
نعم
Inflow and outflow of health personnel
[INFOxNRI12]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx7]
تدفقات العاملين الصحيين الوافدين والمغادرين
[Q11]
هل لديكم آلية لرصد تدفق العاملين الصحيين الوافدين إلى بلدكم والمغادرين لبلدكم؟ (ضع علامة على كل ما ينطبق)
تدفق الوافدين
تدفق المغادرين
لا
[Q11xI]
إذا كانت الإجابة 'نعم' فيما يتعلق بتدفق الوافدين:
[Q11x1]
كم عدد العاملين الصحيين المدربين في الخارج أو المولودين في الخارج الذين بدأوا نشاطهم حديثاً (على نحو مؤقت و/أو دائم) في بلدكم في السنوات الثلاث الماضية (تدفق الوافدين)؟
| أطباء | ممرضون | قابلات | أطباء أسنان | صيادلة | التعليقات | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 42 | 4 | 3 | 9 | 0 | |
| 2022 | 130 | 51 | 0 | 45 | 3 | |
| 2023 | 92 | 58 | 2 | 32 | 16 | |
| مصدر البيانات (السلطة التنظيمية أو سجلات الهجرة أو تصاريح العمل، مثلاً، وما إلى ذلك) | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses and Compulsory Health Insurance Fund Information System, licenced specialists | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses and Compulsory Health Insurance Fund Information System, licenced specialists | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses |
[Q11x3]
إذا كانت لديك أي وثيقة تتضمن معلومات عن تدفقات العاملين الصحيين الوافدين والمغادرين، فيرجى تحمليها.
Stock of health personnel
[INFOxNRI13]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx8]
عدد العاملين الصحيين
[Q12x1]
العدد المجمّع للعاملين الصحيين، مصنفاً حسب بلد التدريب وبلد المولد
فيما يتعلق بآخر سنة متاحة، وبما يتسق مع المؤشرين 1-07 و1-08 لحسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية، يُرجى تقديم معلومات عن العدد الإجمالي للعاملين الصحيين في بلدك (يفضل عدد القوى العاملة النشطة)، مصنفاً حسب مكان التدريب (للمدربين في الخارج) ومكان الميلاد (للمولودين في الخارج).
فيما يتعلق بآخر سنة متاحة، وبما يتسق مع المؤشرين 1-07 و1-08 لحسابات القوى العاملة الصحية الوطنية، يُرجى تقديم معلومات عن العدد الإجمالي للعاملين الصحيين في بلدك (يفضل عدد القوى العاملة النشطة)، مصنفاً حسب مكان التدريب (للمدربين في الخارج) ومكان الميلاد (للمولودين في الخارج).
[Q12x1a]
يُرجى إدراج بيانات عن عدد العاملين الصحيين النشطين في بلدكم بإحدى الطرق التالية:
املأ الجدول الوارد أدناه
[Q12x1x1]
| أطباء (ممارسون عامون + أخصائيون) | 17421 | 17101 | 186 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||
| ممرضون | 26769 | 26492 | 216 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||
| قابلات | 1089 | 1084 | 5 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||
| أطباء أسنان | 4806 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||||
| صيادلة | 3536 | 3515 | 19 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 |
[Q12x1x1x]
إذا كانت لديك أي وثيقة تتضمن معلومات عن عدد العاملين الصحيين النشطين في بلدك وتوزيعهم حسب مكان التدريب ومكان الميلاد، فيرجى تحمليها.
[Q12x2]
يُرجى إدراج بيانات عن البلدان العشرة التي تتصدر بلدان التدريب للعاملين الصحيين المدربين في الخارج في بلدك.
يمكن تقديم هذه المعلومات من خلال أحد الخيارين التاليين:
يمكن تقديم هذه المعلومات من خلال أحد الخيارين التاليين:
املأ الجدول الوارد أدناه
[Q12x2x1]
| أطباء | ممرضون | قابلات | أطباء أسنان | صيادلة | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| مجموع العاملين المدربين في الخارج | 186 | 216 | 5 | 19 | |
| بلد 1 : بلد التدريب | UKR | UKR | UKR | UKR | |
| بلد 1 : عدد العاملين | 103 | 103 | 2 | 16 | |
| بلد 2 : بلد التدريب | RUS | RUS | RUS | RUS | |
| بلد 2 : عدد العاملين | 25 | 35 | 2 | 3 | |
| بلد 3 : بلد التدريب | BLR | BLR | BLR | ||
| بلد 3 : عدد العاملين | 36 | 38 | 1 | ||
| بلد 4 : بلد التدريب | EST | POL | |||
| بلد 4 : عدد العاملين | 7 | 15 | |||
| بلد 5 : بلد التدريب | KAZ | LVA | |||
| بلد 5 : عدد العاملين | 4 | 17 | |||
| بلد 6 : بلد التدريب | AZE | ||||
| بلد 6 : عدد العاملين | 2 | ||||
| بلد 7 : بلد التدريب | |||||
| بلد 7 : عدد العاملين | |||||
| بلد 8 : بلد التدريب | |||||
| بلد 8 : عدد العاملين | |||||
| بلد 9 : بلد التدريب | |||||
| بلد 9 : عدد العاملين | |||||
| بلد 10 : بلد التدريب | |||||
| بلد 10 : عدد العاملين | |||||
| المصدر (السجل المهني، أو بيانات التعداد، أو المسح الوطني، مثلاً، أو غير ذلك) | |||||
| سنة البيانات (يُرجى إدراج بيانات آخر سنة متاحة) | 2023 | 2023 | 2023 | 2023 | |
| ملاحظات |
[Q12x2x1x]
إذا كانت لديك أي وثيقة تتضمن معلومات عن توزيع العاملين الصحيين في بلدك الذين تلقوا تدريبهم في الخارج حسب بلد التدريب، فيرجى تحمليها.
Technical and financial support
[INFOxNRI14]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx9]
الدعم التقني والمالي
[Q13]
هل قدم بلدك مساعدة تقنية أو مالية إلى أي بلد من بلدان المصدر أو البلدان المدرجة في قائمة منظمة الصحة العالمية لدعم وضمانات القوى العاملة الصحية لعام 2023، أو إلى بلدان أخرى منخفضة أو متوسطة الدخل بشأن تنمية القوى العاملة الصحية، أو تعزيز النظام الصحي، أو لتنفيذ توصيات المدونة الأخرى (مثل تعزيز البيانات والمعلومات والبحوث المتعلقة بالقوى العاملة الصحية كي تُترجم إلى سياسات وتخطيط، وما إلى ذلك.)
لا
[Q14]
هل تلقى بلدك مساعدة تقنية أو مالية من أي دولة عضو في منظمة الصحة العالمية أو أصحاب مصلحة آخرين (مثل شركاء التنمية والوكالات الأخرى)، بشأن تنمية القوى العاملة الصحية، أو تعزيز النظام الصحي، أو لتنفيذ توصيات المدونة الأخرى (مثل تعزيز البيانات والمعلومات والبحوث المتعلقة بالقوى العاملة الصحية كي تترجم إلى سياسات وتخطيط، وما إلى ذلك)؟
نعم
[Q14x]
يُرجى تقديم المزيد من المعلومات أدناه (ضع علامة على كل ما ينطبق):
دعم تنمية القوى العاملة الصحية (التخطيط والتعليم والتوظيف والاستبقاء)
دعم العناصر الأخرى لتعزيز النظام الصحي (تقديم الخدمات؛ ونظم المعلومات الصحية؛ وتمويل الصحة؛ والمنتجات والتكنولوجيا الطبية؛ والقيادة الصحية والحوكمة)
مجالات الدعم الأخرى:
[Q14x1]
دعم تنمية القوى العاملة الصحية (التخطيط والتعليم والتوظيف والاستبقاء)
| البلد/ الكيان المقدم للدعم | نوع الدعم (يُرجى التحديد) | |
|---|---|---|
| Europe Union | Lithuania has accessed significant financial support from European Union (EU) structural funds for health system strengthening. These funds have been used to improve healthcare infrastructure, enhance the skills of the health workforce, and implement various health reforms aimed at increasing efficiency and quality in the healthcare system. | |
| Nordic Countries | Partnerships with Nordic Countries: Lithuania has engaged in partnerships with Nordic countries, particularly through the Nordic Council of Ministers, for collaborative projects focused on health system strengthening and workforce development. These partnerships often involve sharing best practices, training, and capacity building. | |
| Norway, Sweden and Germany | Lithuania has also received support from various development partners, including bilateral assistance from countries like Norway, Sweden, and Germany. These countries have provided both technical expertise and funding for projects related to health workforce development, including training programs, exchange of knowledge, and implementation of health system reforms. | |
[Q14x2]
دعم العناصر الأخرى لتعزيز النظام الصحي (تقديم الخدمات؛ ونظم المعلومات الصحية؛ وتمويل الصحة؛ والمنتجات والتكنولوجيا الطبية؛ والقيادة الصحية والحوكمة)
| البلد/ الكيان المقدم للدعم | نوع الدعم (يُرجى التحديد) | |
|---|---|---|
| Europe Union | Technical support was received in the form of COVID-19 tests, vaccines, and other technical tools to facilitate the work of healthcare professionals during the pandemic. | |
Constraints, Solutions, and Complementary Comments
[INFOxNRI15]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[INFOx10]
العقبات والحلول والتعليقات التكميلية
[Q15]
يُرجى ذكر العقبات الثلاثة الرئيسية التي تقف في سبيل الإدارة الأخلاقية للهجرة الدولية في بلدك حسب ترتيب أولويتها، واقتراح الحلول الممكنة:
| العقبات الرئيسية | الحلول/ التوصيات الممكنة | |
|---|---|---|
| Social Integration and Public Perception | Public Awareness Campaigns: Implement targeted campaigns to promote the benefits of migration and multiculturalism, emphasizing success stories and contributions of migrants. | |
| Policy and Legal Framework | Policy Reform: Update and harmonize migration laws to align with international human rights standards, ensuring that they are flexible enough to respond to evolving migration patterns. International Cooperation: Strengthen bilateral and multilateral agreements with source countries to manage migration flows more effectively and humanely. | |
| Economic Integration | Recognition of Qualifications: Simplify and streamline the process for recognizing foreign qualifications and work experience, allowing migrants to work in their trained professions. Entrepreneurship Support: Provide resources, mentoring, and financial support for migrants interested in starting their own businesses, which can create jobs and stimulate the local economy. |
[Q16]
ما هو الدعم الذي تحتاجون إليه لتعزيز تنفيذ المدونة؟
الدعم لتعزيز البيانات والمعلومات المتعلقة بالعاملين الصحيين
1. Enhanced Data Collection Systems Develop Comprehensive Databases: Create or improve national health personnel databases that capture detailed and up-to-date information on the workforce, including demographics, qualifications, and employment status. Implement Standardized Data Collection Tools: Use standardized tools and methods for collecting data across different regions and institutions to ensure consistency and comparability. 2. Data Analysis and Reporting Build Analytical Capacity: Train staff in data analysis techniques to interpret health workforce data effectively, identify trends, and make data-dr,iven decisions. Generate Regular Reports: Produce and disseminate regular reports on health personnel statistics, including workforce distribution, shortages, and migration patterns. 3. Integration with Health Information Systems Link Data Systems: Integrate health personnel data with broader health information systems to provide a comprehensive view of health service delivery and needs. Ensure Interoperability: Ensure that data systems are interoperable with international databases and frameworks to facilitate comparison and coordination. 4. Data Quality and Validation Implement Quality Assurance Measures: Establish procedures for data validation and quality assurance to ensure the accuracy and reliability of health personnel data. Conduct Regular Audits: Perform regular audits of data collection processes and systems to identify and address issues affecting data quality. 5. Capacity Building and Training Train Data Collectors and Analysts: Provide training for personnel involved in data collection and analysis to enhance their skills and understanding of best practices. Develop Data Management Skills: Offer courses and workshops on data management, including the use of advanced data analysis tools and techniques. 6. Access to Technology and Tools Provide IT Infrastructure: Ensure that health institutions have access to the necessary IT infrastructure and software for effective data collection and management. Support Innovative Solutions: Encourage the adoption of innovative technologies such as mobile data collection apps and cloud-based systems to streamline data processes. 7. Collaboration and Partnerships Engage with International Organizations: Collaborate with international organizations and agencies to access best practices, benchmarks, and support for data initiatives. Foster Interinstitutional Cooperation: Promote cooperation between different institutions and agencies involved in health workforce data collection and management. 8. Public Awareness and Transparency Share Data Publicly: Increase transparency by making health workforce data publicly available, where appropriate, to support accountability and informed decision-making. Promote Data Literacy: Raise awareness about the importance of data and its role in improving health systems, and encourage stakeholders to use data in planning and policy development. 9. Policy and Regulatory Support Establish Data Governance Policies: Develop and implement policies for data governance, including data privacy, security, and ethical considerations. Create Data Standards: Define and enforce standards for data collection, reporting, and analysis to ensure consistency and quality.
الدعم للحوار بشأن السياسات وللتنمية
الدعم لإبرام اتفاقات ثنائية/ متعددة الأطراف
أُخرى
لا يلزم الدعم
[Q17]
نظراً إلى أن المدونة تُعد وثيقة دينامية ينبغي تحديثها حسب الاقتضاء، يُرجى تقديم أفكار من بلدك بالاستناد إلى السنوات الأربع عشرة التي مضت منذ صدور القرار الخاص بالمدونة.
[Q17x1]
يُرجى التعليق على مدى فائدة المدونة لبلدك/ كيف كانت مفيدة له.
Evolving Policy and Regulatory Framework
Adoption and Integration:
Since the adoption of the Code in 2010, Lithuania has progressively integrated its principles into national policies. This has involved aligning local regulations with the Code’s recommendations to ensure ethical recruitment practices and prevent the migration of health personnel from low-resource settings.
Regulatory Updates:
The legal framework has been periodically updated to better align with the Code’s recommendations. This includes regulations governing international recruitment, professional standards, and measures to avoid practices that could negatively impact developing countries.
Enhancing Domestic Workforce Capacity
Training and Education:
Efforts have been made to improve the education and training of domestic health personnel to reduce dependency on international recruitment. This includes expanding medical education opportunities and increasing the capacity of training institutions.
Professional Development:
Continuous professional development programs have been established to ensure that health personnel are equipped with the latest skills and knowledge, thus enhancing the quality of care and reducing the need for international recruitment.
Ethical Recruitment Practices
Monitoring and Compliance:
The country has implemented mechanisms to monitor compliance with ethical recruitment practices. This involves ensuring that recruitment agencies and employers adhere to standards that prevent the exploitation of health personnel from developing countries.
International Collaboration:
Lithuania has engaged in international cooperation to share best practices and collaborate on initiatives that support the Code’s objectives. This includes working with global health organizations and participating in international forums.
Addressing Domestic Needs and Retention
Incentives and Retention Strategies:
To address shortages and retain domestic health personnel, various incentives have been introduced, such as financial benefits, career development opportunities, and improved working conditions.
Public Awareness and Recognition:
Efforts to enhance the social recognition of health professions and promote career paths in healthcare have been undertaken. This includes public campaigns to highlight the value of health workers and their contributions to society.
Evaluating Impact and Adjusting Strategies
Regular Review and Feedback:
The impact of the Code’s implementation has been regularly reviewed through feedback mechanisms, including surveys and evaluations of recruitment practices and workforce conditions. This has helped to identify areas for improvement and adjust strategies accordingly.
Adaptation to Emerging Challenges:
The dynamic nature of the Code has necessitated periodic adjustments to national policies and strategies to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the global health workforce landscape.
[Q17x2]
هل يلزم تحديث أي مادة من مواد المدونة؟
لا
[Q17x3]
هل يلزم تحديث عملية الإبلاغ عن تنفيذ المدونة واستعراض مدى ملاءمتها وفعّاليتها؟
لا
[Q17x4]
يُرجى التعليق على قائمة منظمة الصحة العالمية لدعم وضمانات القوى العاملة الصحية (إذا كان بلدك مدرجاً في القائمة، مثلاً، كيف أثر ذلك عليكم؛ إذا كان بلدك لا يعتمد على العاملين الصحيين الدوليين، كيف أثرت القائمة عليكم؛ وإذا لم يكن بلدك مدرجاً في القائمة، كيف أثر ذلك عليكم؟)
[Q18]
أدرج أي تعليقات أو مواد تكميلية أخرى قد ترغب في تقديمها بشأن توظيف العاملين الصحيين وهجرتهم على المستوى الدولي، فيما يتعلق بتنفيذ المدونة.
يُرجى التوضيح أو تحميل الوثيقة (الحجم الأقصى للملف 10 ميغابايت)
يُرجى التوضيح أو تحميل الوثيقة (الحجم الأقصى للملف 10 ميغابايت)
[Q18x1]
Warning
[INFOxNRI16]
أداة الإبلاغ الوطني (2024)
[WARN]
لقد وصلت إلى نهاية أداة إعداد التقارير الوطنية - 2024. يمكنك العودة إلى أي سؤال لتحديث إجاباتك أو تأكيد إدخالك بالنقر فوق 'إرسال'.
