Instrument national de notification (2024)
Background
Adopté en 2010 lors de la Soixante-Troisième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé (résolution WHA 63.16), le Code de pratique mondial de l’OMS pour le recrutement international des personnels de santé (« le Code ») vise à renforcer la compréhension et la gestion éthique du recrutement international des personnels de santé grâce à l’amélioration des données, des informations et de la coopération internationale.
Aux termes de l’article 7 du Code, chaque État Membre de l’OMS devrait échanger des informations concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé. Le Directeur général de l’OMS doit faire rapport tous les trois ans à l’Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
Les États Membres de l’OMS ont achevé le quatrième cycle de notification nationale en mai 2022. Le Directeur général de l’OMS a rendu compte des progrès accomplis dans la mise en œuvre à la Soixante-Quinzième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé en mai 2022 (A75/14). Le rapport sur le quatrième cycle a souligné la nécessité d’évaluer les implications de l’émigration de personnels de santé dans le contexte de l’augmentation des vulnérabilités provoquée par la pandémie de COVID-19. À cette fin, le Groupe consultatif d’experts sur l’utilité et l’efficacité du Code (A73/9) a été convoqué à nouveau. Conformément aux recommandations du Groupe consultatif d’experts, le Secrétariat a publié la Liste OMS d’appui et de sauvegarde pour les personnels de santé 2023.
L’Instrument national de notification (INN) est un outil d’autoévaluation à la disposition des pays pour l’échange d’informations et le suivi du Code. Il permet à l’OMS de recueillir et de partager des données probantes et des informations actuelles concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé. Les conclusions du cinquième cycle de notification nationale seront présentées au Conseil exécutif (EB156) en janvier 2025 en préparation de la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
La date limite de présentation des rapports est fixée au 31 août 2024.
Aux termes de l’article 9 du Code, le Directeur général de l’OMS est chargé de soumettre périodiquement un rapport à l’Assemblée mondiale de la Santé pour indiquer dans quelle mesure le Code permet d’atteindre les objectifs qui y sont fixés et faire des suggestions d’amélioration. En 2024, un groupe consultatif d’experts dirigé par les États Membres se réunira pour le troisième examen du Code. Le rapport de l’examen sera présenté à la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
Pour toute question ou clarification concernant la façon de remplir le questionnaire en ligne, veuillez nous contacter à l’adresse suivante : WHOGlobalCode@who.int.
Qu’est-ce que le Code de pratique mondial de l’OMS ?
Clause de non-responsabilité : Les données et les informations collectées dans le cadre de l’instrument national de notification seront rendues publiques dans la base de données relative à l’INN (https://www.who.int/teams/health-workforce/migration/practice/reports-database) à l’issue des travaux de la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé. Les données quantitatives serviront à alimenter le portail de données sur les comptes nationaux des personnels de santé (http://www.apps.who.int/nhwaportal/).
Disclaimer
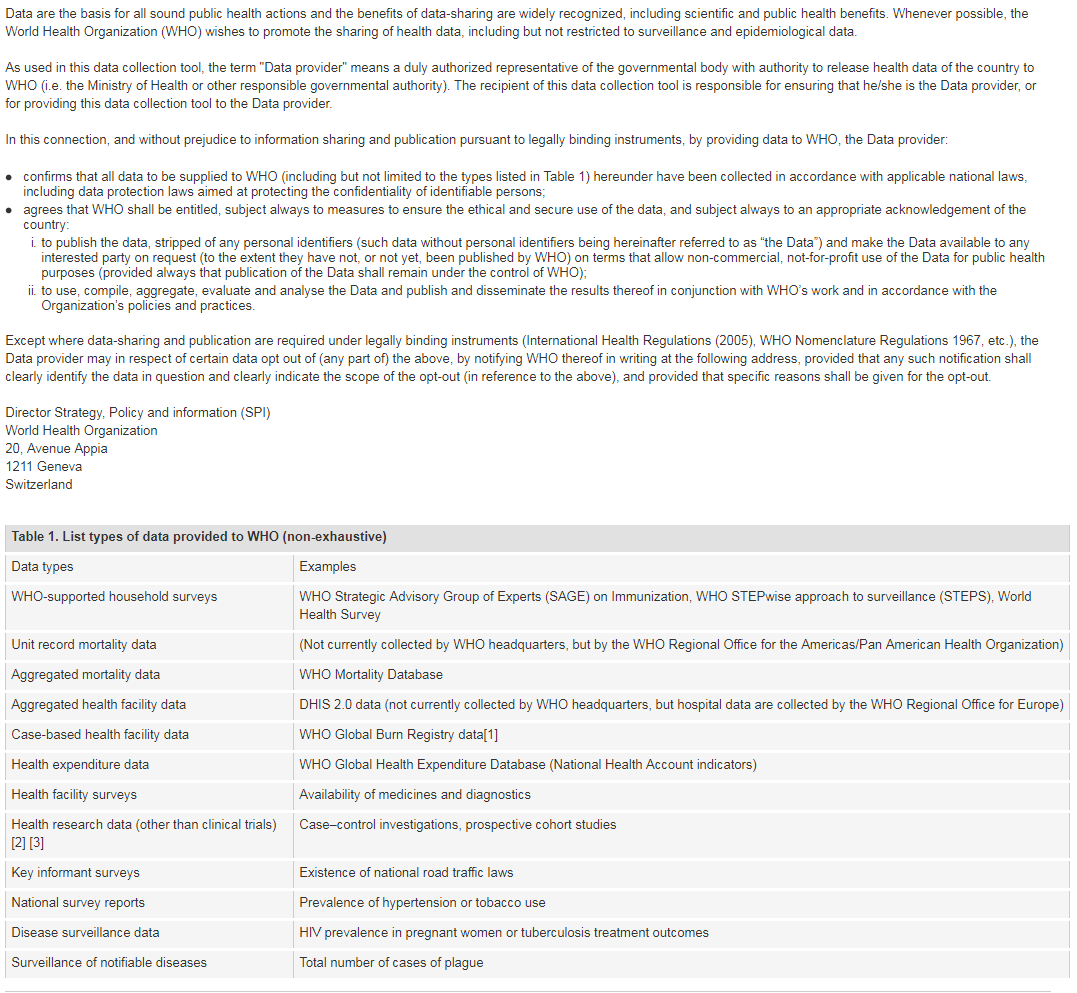
[1] Note: Case-based facility data collection as that in the WHO Global Bum Registry does not require WHO Member State approval.
[2] The world health report 2013: research for universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013 (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85761/2/9789240690837_eng.pdf)
[3] WHO statement on public disclosure of clinical trial results: Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015 (http://www.who.int/ictrp/results/en/, accessed 21 February 2018).
For more information on WHO Data Policy kindly refer to http://www.who.int/publishing/datapolicy/en/
Contact Details
Contemporary issues
International recruitment of health personnel has grown interests in Indonesia, especially due to global demand. In the past three years, the statistics have marked a significant increase. In 2022, the Ministry of Health (MoH) data indicates 958 Indonesian nurses have been deployed as health professional migrants. This number has increased to 1,091 as of 2024, with Japan, Germany, Kuwait, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and Singapore as the countries for destinations. Starting from the bilateral agreement with Japan, in 2022 Indonesia and Germany also established a bilateral agreement to send Indonesian nurses to Germany. The following year, Indonesia and The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) also signed an agreement to send Indonesian nurses and midwives to work in government hospitals in KSA. On the other hand, following the new policy on the competency evaluation for international medical graduates, the MoH introduced an adaptation program for Indonesian medical graduates overseas to return and practice in Indonesia. The MoH also introduced a new mechanism to allow recruitment of foreign health professionals to practice in Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in 2023.
Health Personnel Education
Veuillez télécharger le doccument:
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Government Agreements
| a. Titre de l’accord | b. Type d’accord | |
|---|---|---|
| Accord 1 | MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi” | 1 |
| Accord 2 | MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany | 1 |
| Accord 3 | MOU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and Ministry of KSA | 1 |
| Accord 4 | ||
| Accord 5 | ||
| Accord 6 | ||
| Accord 7 | ||
| Accord 8 | ||
| Accord 9 | ||
| Accord 10 | ||
| Accord 11 | ||
| Accord 12 | ||
| Accord 13 | ||
| Accord 14 | ||
| Accord 15 |
Government Agreements - 6.1 A
| Éducation et formation | Coopération dans le domaine de la santé | Promotion de la migration circulaire | Philanthropie ou appui technique | Reconnaissance des qualifications | Recrutement des personnels de santé | Commerce de services | Autre | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi” | 1 | |||||||
| MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany | 1 | |||||||
| MOU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and Ministry of KSA | 1 | |||||||
| Médecins | Personnel infirmier | Sages-femmes | Dentistes | Pharmaciens | Autres (préciser au besoin) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi” | 1 | 1 | ||||
| MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany | 1 | |||||
| MOU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and Ministry of KSA | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Année de début | Année de fin | |
|---|---|---|
| MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi” | 2008 | present |
| MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany | 2022 | present |
| MOU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and Ministry of KSA | 2023 | present |
Government Agreements - 6.1 B
| Première année de mise en œuvre: | |
|---|---|
| MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi” | 2008 |
| MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany | 2022 |
| MOU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and Ministry of KSA | |
Accord: MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi”
| Nombre de personnels | |
|---|---|
| Médecins | |
| Personnel infirmier | 3059 |
| Sages-femmes | 40 |
| Dentistes | |
| Pharmaciens | |
Accord: MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany
| Nombre de personnels | |
|---|---|
| Médecins | |
| Personnel infirmier | 194 |
| Sages-femmes | |
| Dentistes | |
| Pharmaciens | |
| Télécharger document(s) | |
|---|---|
| MoU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and the Japan International Corporation of Welfare Services on the Deployment and Acceptance of Indonesia Candidatefor “Kangoshi”, Indonesian Candidate for “Kaigofukushisi”, Indonesian “Kangoshi” and Indonesia “Kaigofukushisi” | |
| MoU on Labour and Employment between Ministry of Manpower of the Rep of Indonesia and the Bundesagentur fur Arbeit, Germany | |
| MOU between the National Board for the Placement and Protection of Indonesian Overseas Workers and Ministry of KSA | |
Responsibilities, rights and recruitment practices
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
International migration
| Demande directe (individuelle) à des fins d’éducation, d’emploi, de commerce, d’immigration ou d’entrée dans le pays | Accords entre États autorisant la mobilité des personnels de santé | Agences de recrutement privées ou recrutement facilité par l’employeur | Mobilité facilitée par des cabinets de conseil privés spécialisés dans l’éducation/l’immigration | Autres filières (veuillez préciser) | Quelle est la filière la plus utilisée ? Veuillez fournir des données quantitatives si elles sont disponibles. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Médecins | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Personnel infirmier | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Sages-femmes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dentistes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pharmaciens | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Demande directe (individuelle) à des fins d’éducation, d’emploi, de commerce, d’immigration ou d’entrée dans le pays | Accords entre États autorisant la mobilité des personnels de santé | Agences de recrutement privées ou recrutement facilité par l’employeur | Mobilité facilitée par des cabinets de conseil privés spécialisés dans l’éducation/l’immigration | Autres filières (veuillez préciser) | Quelle est la filière la plus utilisée ? Veuillez fournir des données quantitatives si elles sont disponibles. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Médecins | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Personnel infirmier | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Sages-femmes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Dentistes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pharmaciens | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Recruitment & migration
Il est essentiel d’améliorer la disponibilité et la comparabilité internationale des données pour comprendre et gérer les dynamiques mondiales des migrations des agents de santé. Veuillez consulter votre point focal CNPS, le cas échéant, pour vous assurer que les données rapportées ci-dessous sont conformes aux rapports CNPS*.
(Pour plus de détails sur le point focal CNPS de votre pays, veuillez consulter la version électronique de l’INN ou contacter WHOGlobalCode@who.int)
Inflow and outflow of health personnel
| Médecins | Personnel infirmier | Sages-femmes | Dentistes | Pharmaciens | Remarques | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||||
| 2022 | 50 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 2023 | 50 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Source des données (p. ex., organisme de réglementation, dossiers d’immigration, permis de travail, etc.) |
| Médecins | Personnel infirmier | Sages-femmes | Dentistes | Pharmaciens | Remarques | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 469 | |||||
| 2022 | 1300 | |||||
| 2023 | 1415 | 19 | ||||
| Source des données (p. ex., organisme de réglementation, dossiers d’immigration, permis de travail, etc.) | 682 | 21 |
Stock of health personnel
Pour la dernière année disponible, conformément aux indicateurs 1-07 et 1-08 des comptes nationaux des personnels de santé (CNPS), veuillez fournir des informations sur le stock total de personnels de santé dans votre pays (de préférence la main-d’œuvre active), ventilées par lieu de formation (formés à l’étranger) et par lieu de naissance (nés à l’étranger).
| Médecins (généralistes + spécialistes) | 213.203 | 213.154 | 49 | 47 | 2 | 213.201 | 2 | Indonesian Health Council's database | 2024 | 1 | |
| Personnel infirmier | 770.816 | 770.816 | 770.816 | Indonesian Health Council's database | 2024 | 1 | |||||
| Sages-femmes | 541.258 | 541.258 | 541.258 | Indonesian Health Council's database | 2024 | 1 | |||||
| Dentistes | 47.301 | 47.301 | 47.301 | Indonesian Health Council's database | 2024 | 1 | |||||
| Pharmaciens | 175.150 | 175.150 | 175.150 | Indonesian Health Council's database | 2024 | 1 |
Ces informations peuvent être fournies par l’un des deux moyens suivants:
| Médecins | Personnel infirmier | Sages-femmes | Dentistes | Pharmaciens | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total des personnels formés à l’étranger | |||||
| Pays 1: Pays de formation | PHL | ||||
| Pays 1: Nombre de personnels | 34 | ||||
| Pays 2: Pays de formation | CHN | ||||
| Pays 2: Nombre de personnels | 5 | ||||
| Pays 3: Pays de formation | DEU | ||||
| Pays 3: Nombre de personnels | 3 | ||||
| Pays 4: Pays de formation | USA | ||||
| Pays 4: Nombre de personnels | 2 | ||||
| Pays 5: Pays de formation | JPN | ||||
| Pays 5: Nombre de personnels | 1 | ||||
| Pays 6: Pays de formation | AUS | ||||
| Pays 6: Nombre de personnels | 1 | ||||
| Pays 7: Pays de formation | MYS | ||||
| Pays 7: Nombre de personnels | 1 | ||||
| Pays 8: Pays de formation | NPL | ||||
| Pays 8: Nombre de personnels | 1 | ||||
| Pays 9: Pays de formation | GBR | ||||
| Pays 9: Nombre de personnels | 1 | ||||
| Pays 10: Pays de formation | |||||
| Pays 10: Nombre de personnels | |||||
| Source (par ex. registre professionnel, données de recensement, enquête nationale, autres) | |||||
| Année de collecte des données (Veuillez fournir les données correspondant à la dernière année disponible) | 2022 - 2024 | ||||
| Observations |
Technical and financial support
| Pays bénéficiant d’un appui | Type d’appui (veuillez préciser) | |
|---|---|---|
| Vanuatu | Training 20 nurses in Basic Trauma and Cardiac Life Support (BTCLS) and Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance, implemented in: 4 – 16 November 2024. | |
| Fiji | Indonesian AID Scholarship (TIAS) 2024 to support one student from Fiji enrolled in the Bachelor of Nursing in Applied Science program at the Poltekkes Kemenkes Surakarta. | |
| Solomon Island | Indonesian AID Scholarship (TIAS) 2024 to support one student from Solomon Island enrolled in the Bachelor of Nursing in Applied Science program at the Poltekkes Kemenkes Surakarta. | |
| Kenya | Indonesian AID Scholarship (TIAS) 2024 to support one student from Kenya enrolled in the Bachelor of Nursing in Applied Science program at the Poltekkes Kemenkes Surakarta. |
| Pays bénéficiant d’un appui | Type d’appui (veuillez préciser) | |
|---|---|---|
| Papua New Guinea | Humanitarian Assistance for landslides in Yambali and Kaokalam, Enga Province, Papua New Guinea. As many as 8,135 kg of supplies, in the forms of food, and malaria medicine was shipped on 8 July 2024. | |
| Pacific Islands | Medicines were carried along with the National Marine Corps’ (TNI AL) visits to South Pacific countries in October 2024. | |
| Türkiye | Emergency Medical Team was deployed for humanitarian aid following a great earthquake in Türkiye 2023. | |
| Pays/entité à l’origine de l’appui | Type d’appui (veuillez préciser) | |
|---|---|---|
| World Health Organization (WHO) | (1) Increase production of essential health professionals via MOH Polytechnics. (2) Improve distribution and retention of health workers by developing policy briefs on workforce distribution. (3) Enhance workforce quality through improvements in human resources for health (HRH) planning, information systems, education, and professional development. | |
| Goethe Institut Germany | Curriculum development for nursing undergraduate programme, emphasizing on cultural competency and German language acquisition to prepare 30 nursing graduates per year from each health polytechnic for international recruitment in Germany under either the national or private placement schemes. This initiative aims to equip graduates with the essential skills and knowledge required for seamless integration into the German healthcare system | |
| World Bank DFAT Trust Fund | Development of an Academic Health System to expand and enhance Indonesia’s capacity to train and produce specialized medical professionals. | |
| Pays/entité à l’origine de l’appui | Type d’appui (veuillez préciser) | |
|---|---|---|
| UNFPA | Providing resources and guidance to develop specialized health services, particularly in reproductive and maternal health. | |
| Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) | Funding to enhance caregiver competencies, equipping healthcare providers with specialized skills to address the needs of Indonesia’s aging population. | |
| Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA) | Conducting disaster response management training programs in five provinces. Budget: Grant aid of USD 12,000,000 for disaster management capacity building. | |
| Governance Agreement (GA) MOH & IHME | Establishing a Joint Project Office with expected outputs of: (1) Estimation of key health indicators and projected burden for over 300 diseases and 80 risk factors across provinces and districts/cities through to 2050. (2) Quantification of healthcare system capacity, including forecasting healthcare human resources by profession and specialization for each province through to 2050. (3) Assessment of healthcare human resource needs and other healthcare system capacities. (4) Customized visualizations tailored to local needs to communicate findings and make results accessible to stakeholders at various levels. (5) Development of analytical capacity in Indonesia, training in the application of Global Burden of Disease techniques, and enabling sustainable local estimation efforts. |
Constraints, Solutions, and Complementary Comments
| Principaux obstacles | Solutions/recommandations envisageables | |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Data on Migrant Health Personnel | Develop a centralized database to track health personnel migration patterns, employment conditions, and return rates through SATU SEHAT. This system would support evidence-based policymaking and help monitor the ethical recruitment of health personnel. | |
| Insufficient Policy Coordination Across Sectors | Establish an inter-ministerial committee to ensure coordination between health, labor, and immigration sectors. Regular meetings and collaborative planning would strengthen policy coherence and improve the ethical management of health personnel migration | |
| Lack of Bilateral Agreements with Key Destination Countries | Negotiate bilateral agreements with countries that employ a significant number of Indonesian health personnel. These agreements should outline standards for fair treatment, safe working conditions, and pathways for skill recognition, benefiting both migrant workers and the Indonesian health system. |
Yes. As the global healthcare landscape evolves, it may be beneficial to update articles in the Code to address new challenges in digital health, telemedicine, and cross-border healthcare service provision. Including guidelines on virtual employment of health personnel could enhance the Code's relevance.
Yes. The reporting process should be updated with a more user-friendly and simpler data collection and sharing tools. Annual reviews that involve feedback from a broader group of stakeholders, including migrant health workers themselves, would provide a more comprehensive assessment of the Code's impact and its areas for improvement.
Veuillez expliquer OU télécharger un document (taille maximale du fichier 10 Mo)
