Instrument national de notification (2024)
Background
[INFOxNRI1]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[BGxINT]
Contexte
Adopté en 2010 lors de la Soixante-Troisième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé (résolution WHA 63.16), le Code de pratique mondial de l’OMS pour le recrutement international des personnels de santé (« le Code ») vise à renforcer la compréhension et la gestion éthique du recrutement international des personnels de santé grâce à l’amélioration des données, des informations et de la coopération internationale.
Aux termes de l’article 7 du Code, chaque État Membre de l’OMS devrait échanger des informations concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé. Le Directeur général de l’OMS doit faire rapport tous les trois ans à l’Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
Les États Membres de l’OMS ont achevé le quatrième cycle de notification nationale en mai 2022. Le Directeur général de l’OMS a rendu compte des progrès accomplis dans la mise en œuvre à la Soixante-Quinzième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé en mai 2022 (A75/14). Le rapport sur le quatrième cycle a souligné la nécessité d’évaluer les implications de l’émigration de personnels de santé dans le contexte de l’augmentation des vulnérabilités provoquée par la pandémie de COVID-19. À cette fin, le Groupe consultatif d’experts sur l’utilité et l’efficacité du Code (A73/9) a été convoqué à nouveau. Conformément aux recommandations du Groupe consultatif d’experts, le Secrétariat a publié la Liste OMS d’appui et de sauvegarde pour les personnels de santé 2023.
L’Instrument national de notification (INN) est un outil d’autoévaluation à la disposition des pays pour l’échange d’informations et le suivi du Code. Il permet à l’OMS de recueillir et de partager des données probantes et des informations actuelles concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé. Les conclusions du cinquième cycle de notification nationale seront présentées au Conseil exécutif (EB156) en janvier 2025 en préparation de la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
La date limite de présentation des rapports est fixée au 31 août 2024.
Aux termes de l’article 9 du Code, le Directeur général de l’OMS est chargé de soumettre périodiquement un rapport à l’Assemblée mondiale de la Santé pour indiquer dans quelle mesure le Code permet d’atteindre les objectifs qui y sont fixés et faire des suggestions d’amélioration. En 2024, un groupe consultatif d’experts dirigé par les États Membres se réunira pour le troisième examen du Code. Le rapport de l’examen sera présenté à la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
Pour toute question ou clarification concernant la façon de remplir le questionnaire en ligne, veuillez nous contacter à l’adresse suivante : WHOGlobalCode@who.int.
Qu’est-ce que le Code de pratique mondial de l’OMS ?
Clause de non-responsabilité : Les données et les informations collectées dans le cadre de l’instrument national de notification seront rendues publiques dans la base de données relative à l’INN (https://www.who.int/teams/health-workforce/migration/practice/reports-database) à l’issue des travaux de la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé. Les données quantitatives serviront à alimenter le portail de données sur les comptes nationaux des personnels de santé (http://www.apps.who.int/nhwaportal/).
Adopté en 2010 lors de la Soixante-Troisième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé (résolution WHA 63.16), le Code de pratique mondial de l’OMS pour le recrutement international des personnels de santé (« le Code ») vise à renforcer la compréhension et la gestion éthique du recrutement international des personnels de santé grâce à l’amélioration des données, des informations et de la coopération internationale.
Aux termes de l’article 7 du Code, chaque État Membre de l’OMS devrait échanger des informations concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé. Le Directeur général de l’OMS doit faire rapport tous les trois ans à l’Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
Les États Membres de l’OMS ont achevé le quatrième cycle de notification nationale en mai 2022. Le Directeur général de l’OMS a rendu compte des progrès accomplis dans la mise en œuvre à la Soixante-Quinzième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé en mai 2022 (A75/14). Le rapport sur le quatrième cycle a souligné la nécessité d’évaluer les implications de l’émigration de personnels de santé dans le contexte de l’augmentation des vulnérabilités provoquée par la pandémie de COVID-19. À cette fin, le Groupe consultatif d’experts sur l’utilité et l’efficacité du Code (A73/9) a été convoqué à nouveau. Conformément aux recommandations du Groupe consultatif d’experts, le Secrétariat a publié la Liste OMS d’appui et de sauvegarde pour les personnels de santé 2023.
L’Instrument national de notification (INN) est un outil d’autoévaluation à la disposition des pays pour l’échange d’informations et le suivi du Code. Il permet à l’OMS de recueillir et de partager des données probantes et des informations actuelles concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé. Les conclusions du cinquième cycle de notification nationale seront présentées au Conseil exécutif (EB156) en janvier 2025 en préparation de la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
La date limite de présentation des rapports est fixée au 31 août 2024.
Aux termes de l’article 9 du Code, le Directeur général de l’OMS est chargé de soumettre périodiquement un rapport à l’Assemblée mondiale de la Santé pour indiquer dans quelle mesure le Code permet d’atteindre les objectifs qui y sont fixés et faire des suggestions d’amélioration. En 2024, un groupe consultatif d’experts dirigé par les États Membres se réunira pour le troisième examen du Code. Le rapport de l’examen sera présenté à la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé.
Pour toute question ou clarification concernant la façon de remplir le questionnaire en ligne, veuillez nous contacter à l’adresse suivante : WHOGlobalCode@who.int.
Qu’est-ce que le Code de pratique mondial de l’OMS ?
Clause de non-responsabilité : Les données et les informations collectées dans le cadre de l’instrument national de notification seront rendues publiques dans la base de données relative à l’INN (https://www.who.int/teams/health-workforce/migration/practice/reports-database) à l’issue des travaux de la Soixante-Dix-Huitième Assemblée mondiale de la Santé. Les données quantitatives serviront à alimenter le portail de données sur les comptes nationaux des personnels de santé (http://www.apps.who.int/nhwaportal/).
Disclaimer
[INFOxNRI2]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[disclaim]
Clause de non-responsabilité
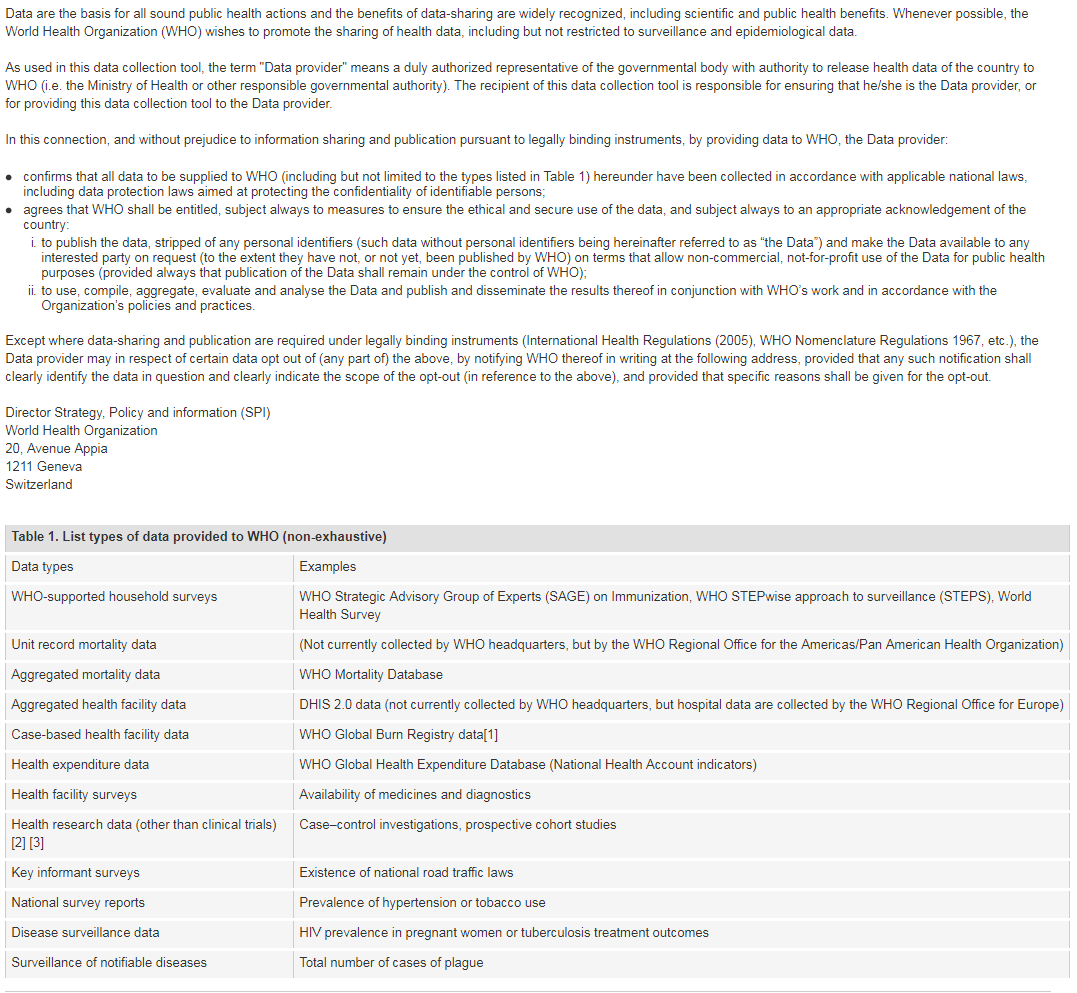
[1] Note: Case-based facility data collection as that in the WHO Global Bum Registry does not require WHO Member State approval.
[2] The world health report 2013: research for universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013 (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85761/2/9789240690837_eng.pdf)
[3] WHO statement on public disclosure of clinical trial results: Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015 (http://www.who.int/ictrp/results/en/, accessed 21 February 2018).
For more information on WHO Data Policy kindly refer to http://www.who.int/publishing/datapolicy/en/

[1] Note: Case-based facility data collection as that in the WHO Global Bum Registry does not require WHO Member State approval.
[2] The world health report 2013: research for universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013 (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85761/2/9789240690837_eng.pdf)
[3] WHO statement on public disclosure of clinical trial results: Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015 (http://www.who.int/ictrp/results/en/, accessed 21 February 2018).
For more information on WHO Data Policy kindly refer to http://www.who.int/publishing/datapolicy/en/
J'ai lu et pris connaissance de la politique de l'OMS relative à l'utilisation et à la communication des données collectées par l'OMS dans les Etats Membres en dehors des urgences de santé publique.
Contact Details
[INFOxNRI3]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[CI]
Coordonnées
Nom de l’État Membre :
Lithuania
Nom de l’autorité nationale désignée :
State Accreditation Service for Health Care Activities
Titre de l’autorité nationale désignée :
Division of Specialist Activities
Institution de l’autorité nationale désignée :
State Accreditation Authority for Health Care under the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Lithuania
Courriel :
riginao@who.int,agne.raukstiene@vaspvt.gov.lt,vaspvt@vaspvt.gov.lt,WHOGlobalCode@who.int
Numéro de téléphone :
+370 653 06363
Contemporary issues
[INFOxNRI4]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[NRIxI]
Les questions marquées d’un * sont obligatoires. Le système ne permettra pas la soumission tant que vous n’aurez pas répondu à toutes les questions obligatoires.
[INFOx1]
Questions actuelles sur les migrations et la mobilité des personnels de santé
[Q1x1]
Au cours des 3 dernières années, la question du recrutement international des personnels de santé a-t-elle été un sujet de préoccupation pour votre pays ?
Non, ce n’est pas un problème dans mon pays
[Q1x2]
Au cours des trois dernières années, la question de la dépendance internationale à l’égard des personnels de santé (recrutement international de personnels de santé pour répondre aux besoins nationaux) a-t-elle été un sujet de préoccupation pour votre pays ?
Non, ce n’est pas un problème dans mon pays
Health Personnel Education
[INFOxNRI5]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx2]
Formation et emploi des personnels de santé, et pérennisation des systèmes de santé
[Q2]
Votre pays prend-il des mesures pour former, employer et fidéliser des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne adaptés aux conditions propres à votre pays, y compris dans les zones les plus démunies ?
Oui
[Q2x1]
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
2.1 Mesures prises pour assurer la pérennité des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne
2.2 Mesures prises pour remédier à la mauvaise répartition géographique des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne et pour les fidéliser*
2.3 Autres mesures pertinentes pour former, employer et fidéliser des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne adaptés aux conditions propres à votre pays
[Q2x1x1]
2.1.1 Mesures prises pour assurer la pérennité des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne
Prévoir les besoins futurs en personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne afin de guider la planification
The Ministry of Health has developed an action plan for the years 2024-2029 aimed at reducing the uneven distribution of healthcare professionals nationwide and addressing shortages of certain professional qualifications and specializations in the healthcare sector. The action plan outlines the following measures: 1. Monitoring of Healthcare Workforce: Implementation of systems to track and monitor the shortage, training, distribution, and recruitment of healthcare professionals. 2. Improvement of Forecasting and Planning: Enhancements in forecasting and planning for healthcare workforce needs. 3. Empowerment, Recruitment, and Retention: Strategies to empower, attract, and retain healthcare professionals. It is planned to prepare an overview of the current situation of health human resources management in Lithuania, analyze best practices from foreign countries, and provide recommendations for human resources management, demand forecasting, inclusion, retention, improvement, and more. Based on these documents, a long-term health human resources management strategy (up to 2030) would be developed and approved at the national level.
Aligner la formation des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne du pays sur les besoins des systèmes de santé
Planned Investments in Training and Professional Development. A budget of 30.7 million euros has been allocated for healthcare professionals recruitment measures from the 2021-2027 European Union funds investment program. These funds will be directed towards: • Enhancing Human Resources Management Efficiency: Improving the efficiency of healthcare human resources management. • Financing Study Costs: Covering the costs of healthcare education. • Empowerment, Recruitment, and Retention Models: Developing and implementing models for the empowerment, recruitment, and retention of healthcare professionals within healthcare institutions. • Increasing Prestige and Professional Orientation: Elevating the prestige and professional orientation of the most critically needed professional qualifications and specializations. • Other Related Initiatives: Additional measures to support the overall recruitment and retention strategy.
Améliorer la qualité de la formation et des personnels de santé en fonction des besoins en prestation de services
Ensuring high-quality healthcare services can only be achieved by adequately trained and educated high-level healthcare professionals. To enhance the quality of residency studies and residency bases across the country, the Ministry of Health will allocate funding for the acquisition and improvement of educational competencies of physician residents' mentors – 344,000 euros have been earmarked for this purpose. On July 31, 2024, Order No. V-788 was issued, titled „Order on the approval of the procedure for updating the educational competencies of the resident physician supervisor and acquiring and updating the educational competencies of the resident physician mentor. “ A project funded by the European Union's 2021–2027 investment program is dedicated to physician resident mentors who will work in healthcare institutions outside the largest cities of Lithuania, including regional areas. The project's goal is to provide these mentors with educational skills to ensure a quality learning process and a positive psycho-emotional climate for physician residents in their residency bases. Additionally, it aims to help young doctors integrate more easily and effectively into the healthcare system. Approved professional development programs are designed for healthcare professionals and administrative staff working in personal healthcare institutions. These programs focus on developing both general (management, leadership, communication, emotional literacy, etc.) and specialized competencies. Based on the Long-Term Care Service Provision Model Development Project Plan, which was approved by the Government in December 2021, a plan for the training, retraining, and professional development of long-term care specialists is to be prepared. A legal act aimed at improving the qualifications and working conditions of healthcare professionals is planned to be drafted. This act will regulate the financing mechanism for the professional development of healthcare professionals, introducing a professional qualification development fund for healthcare professionals, financed by the state, institutions, organizations, and personal funds.
Créer des possibilités d’emploi adaptées aux besoins de la population en matière de santé
Aiming to address the shortage of healthcare professionals in Lithuania's national health system, the Ministry of Health has requested personal healthcare institutions to provide information on their preliminary capabilities to cover the tuition fees of pupils, students, and resident doctors, in accordance with the order of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Lithuania No. V-1080, dated November 7, 2008. Additionally, institutions were asked to provide information on other possible incentive measures for attracting healthcare professionals. The Ministry of Health has compiled lists of incentive measures to present comprehensive information, allowing pupils, students, and resident doctors to find all relevant information in one place and make informed decisions regarding contract agreements with personal healthcare institutions. This list will aid in attracting healthcare professionals with the most needed qualifications to personal healthcare institutions experiencing the greatest shortage of these specialists. These healthcare professionals could contribute to the provision of quality and timely healthcare services, addressing the health needs of the population. Starting from July 1, 2024, a patient transportation service will be launched in Lithuania. Patients who meet the transportation criteria will be able to order the service by calling 1808, from home to the healthcare facility and back. The expansion of this service will bring healthcare services closer to patients and thus help the most vulnerable populations (due to health, poverty, age). The aim of this measure is to ensure that age, level of participation, health status, or other factors do not hinder access to necessary healthcare services.
Gérer le recrutement international des personnels de santé
Lithuania adheres to the principles of the World Health Organization (WHO) Global Code of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel, aiming to ensure ethical and responsible international recruitment of health care professionals. This Code aims to strengthen health systems in developing countries and maintain a balance between the migration of health care professionals and the needs of national health systems. Adherence to Ethical Principles Compliance with the Code: Lithuania is committed to adhering to the WHO Global Code, which sets out ethical principles for the international recruitment of health care professionals, aiming to protect the health systems of developing countries from brain drain. Development of National Strategies Formulating National Policies: The Ministry of Health (SAM) develops national strategies that include measures for the recruitment, training, and retention of health care professionals to ensure that those working in Lithuania meet the country's needs and international standards. International Collaboration Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements: Lithuania collaborates with other countries to ensure fair and responsible recruitment of health care professionals, sharing best practices and information on migration trends. Incentive Programs Incentive Programs: Lithuania implements various incentive measures to retain and attract health care professionals, such as financial support for students, residents, and doctors who commit to working in the country's health care facilities for a specified period. Return Programs Return and Reintegration Programs: Lithuania encourages emigrated health care professionals to return by offering reintegration programs, including professional development, job placements, and financial support. Education and Awareness Information Dissemination: The Ministry of Health and other relevant institutions conduct information campaigns to inform health care professionals about international recruitment rules, opportunities, and responsibilities, as well as the principles of the WHO Code. Challenges and Solutions Shortage of Specialists in Certain Areas Targeted Measures: To address the shortage of specialists, Lithuania implements targeted measures such as financial incentives, professional development programs, and improvements in infrastructure in regional health care facilities. Impact of Migration on the Health System Ensuring Balance: Lithuania strives to maintain a balance between international recruitment of specialists and the needs of the national health system, considering the specifics and priorities of the country's health care sector. Lithuania actively implements measures to ensure responsible international recruitment of health care professionals in accordance with the WHO Global Code of Practice. These measures help strengthen the country's health care system, ensure the sustainability of health care professionals, and contribute to improving public health.
Améliorer la gestion des personnels de santé
The Ministry of Health plans to develop and approve professional qualification enhancement programs for healthcare professionals and administrative staff working in personal health care institutions. These programs will focus on both general (management, leadership, communication, emotional intelligence, etc.) and specific competencies. Training sessions are scheduled to commence from 2024 and continue through 2029. An allocation of €1.8 million from the 2021–2027 European Union funds investment program has been designated for this measure. The planned qualification enhancement will focus on primary care, specialized fields (including emergency and urgent medical care, mental health services), long-term care, and pharmacy. It will also include the requalification of emergency medical specialists. To improve the monitoring and planning of healthcare professionals' qualifications, the development of an IT tool—the Healthcare Professionals Competency Platform—is planned.
Dispositions spécifiques relatives à la réglementation et au recrutement des personnels de santé en situation d’urgence
Plans are underway for the development and modernization of top-level infectious disease cluster centers and regional infectious disease cluster centers, with an emphasis on improving infectious disease management. Two top-level centers are set to be established for the modernization of emergency medical departments in regional hospitals to ensure effective patient flow management and accessibility and quality of emergency medical services during epidemics/pandemics. A systematic strengthening of the health system's resilience to operate in emergencies is planned, with an allocation of €148 million (excluding VAT) for infrastructure development and equipment acquisition. This initiative aims to ensure regional-level infectious disease treatment capacities during crises (at least 650 beds) and create conditions for conducting research on dangerous and highly dangerous infections, integrating into international scientific programs. The goal is to adapt the emergency medical departments and intensive care units of major national hospitals to effectively provide emergency medical services to a large number of patients simultaneously in the event of high and very high-risk incidents, ensuring safe working conditions for staff working under hazardous conditions. Plans are underway to develop legislation aimed at enhancing the preparedness of healthcare institutions for operating in emergencies. The following actions are planned under the modernization action plan for healthcare institutions' collaboration and infrastructure adaptation for emergencies: Requirements Specification: Establish requirements that healthcare institutions must meet to ensure their preparedness for emergencies. Legal Foundations: Create legal frameworks to support healthcare institutions and their personnel in preparing for and operating during emergencies. Resource Cooperation: Develop legal provisions to facilitate more effective cooperation of resources (material and human). From the 2021-2027 EU funds investment program, it is planned to acquire additional vehicles to meet increased demand due to a higher number of emergency medical service stations and the need to transport patients to specialized centers in acute conditions. This includes updating some vehicles due to wear and tear. On January 18, 2024, an Expert Working Group was established to review healthcare professional education programs and to incorporate competencies necessary for preparedness for emergencies and wartime threats into these programs. The tasks of the Expert Working Group are: To identify the competencies required by healthcare sector professionals to provide rapid and coordinated healthcare services during emergencies or wartime (hereinafter referred to as "competencies"). To establish a strategy for the development of these competencies.
Autres
In all cases, the professional qualification of doctors, nurses, dentists, oral care specialists and other regulated professions health care specialists acquired outside the Republic of Lithuania must be recognized in accordance with the Directive 2005/36/EC. Practice shows that the recognition of professional qualification of a medical doctor is recognized by practically all applicants. Problems arise with professional qualification of specialists from third countries, because the duration of studies is often significantly shorter than in Lithuania. During the recognition, the work experience is also assessed. High length of practise sometimes compensates for the shorter duration of studies. Recognition of professional qualifications is only one part of procedure to legally provide personal health care services in Lithuania. Once the professional qualification is recognized, specialist must obtain their license. In order to obtain a license, the conditions for proficiency in the Lithuanian language and permission to temporarily live and work in Lithuania are needed, which often causes problems for individuals.
[Q2x2x1]
Cochez tous les éléments qui s’appliquent pour mesures prises pour remédier à la mauvaise répartition géographique des personnels de santé et d’aide à la personne et pour les fidéliser
2.2.1 Éducation
2.2.2 Réglementation
2.2.3 Incitations
2.2.4 Appui
[Q2x2x1x1]
2.2.1.1 Éducation Mesures
Établissements d’enseignement situés dans des zones rurales/mal desservies
Educational institutions (universities, colleges, and vocational training schools/centers) are in the major cities of the country.
Admission d’étudiants provenant de régions et de communautés rurales/mal desservies
Admissions to educational institutions are carried out according to the general procedure established by the institutions. This procedure allows individuals from rural or underserved areas to apply and be admitted to educational institutions.
Bourses d’études et aides à l’éducation
Thèmes/programmes d’études pertinents dans les programmes d’éducation et/ou de perfectionnement professionnel
(Ré)orientation des programmes d’éducation vers les soins de santé primaires
Autres
[Q2x2x2x1]
2.2.2.1 Réglementation Mesures
Bourses d’études et aides à l’éducation assorties d’accords de service contractuel
According to the Order No. V-1080 of November 7, 2008, by the Minister of Health of the Republic of Lithuania, students, trainees, or medical residents can benefit from a legal framework that regulates financial support from municipal administrations or healthcare institutions. This support is available to those studying in non-state-funded places. By entering into study financing agreements, they are required to fulfill contractual obligations by working for a specified number of years in the healthcare institution, thus contributing to the needed healthcare workforce.
Accords de services obligatoires avec les personnels de santé qui ne sont pas liés à des bourses d’études ou à des aides à l’éducation
Élargissement du champ de pratique des personnels de santé existants
Requalification of Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Specialists Starting January 1, 2024, the new regulations for providing Emergency Medical Services (EMS) will come into effect. According to these regulations, EMS drivers will be required to hold a paramedic professional qualification. This change aims to enhance the capabilities of EMS teams, ensuring that all members, including drivers, are equipped with the necessary medical knowledge and skills to effectively respond to emergencies. Pharmacy Specialist Training To better utilize the potential of pharmacists as competent health care specialists, additional training for pharmacy professionals is planned. This training will focus on expanding the range of patient-centered pharmaceutical care services and advanced practice pharmacy roles. Specifically, the following initiatives are planned: 1. Development of Additional Services: By the second half of 2022, a phased implementation of new services provided by pharmacists will begin. This will continue through to 2030, with new regulations defining these services and their delivery conditions. 2. Competency Requirements: Regulations will outline the competencies required for pharmacists, specifying the necessary training hours, procedures, target patient groups, and collaboration with physicians. 3. Enhanced Pharmaceutical Care: The new services will include comprehensive pharmaceutical care and extended practice roles, which will aim to improve patient outcomes through better medication management and health advice. These measures are intended to strengthen the role of pharmacists in the healthcare system, ensuring that they can provide high-quality, patient-focused services and work effectively within the healthcare team.
Partage des tâches entre les différentes catégories professionnelles
Family Doctor Team Model Comprehensive Family Doctor Team: To improve service quality and accessibility, family medicine services are provided by a comprehensive family doctor team. This team includes a family doctor, nurses, midwife, nurse assistant, physiotherapist, lifestyle medicine specialist, and case manager. Competency Distribution: Functions of team members are allocated according to their expanded competencies, thereby more effectively utilizing the specialists' skills. Retraining of Emergency Medical Services Specialists Paramedic Qualification: From January 1, 2024, following the new Emergency Medical Services provision requirements, emergency medical drivers must have a paramedic professional qualification. Retraining Programs: Training and professional development courses are organized to ensure that emergency medical services specialists are adequately prepared for emergencies. Development of Pharmacy Specialists' Competencies Pharmaceutical Care and Advanced Practice Services: To better utilize pharmacists' potential, additional patient-oriented pharmaceutical care and advanced practice pharmacist (pharmacist-healthcare specialist) services are being developed. Regulation and Training: From the second half of 2022 to 2030, it is planned to gradually regulate additional services provided in pharmacies and their conditions, including the enhancement of pharmacists' competencies. Retraining and Professional Development of Specialists Integrated Health Care Services: Continuous training is organized to improve the competencies of health care specialists, providing new knowledge and practical skills for working with innovative and advanced technologies. Retraining for Internal Medicine and Pediatric Doctors: There are plans to allow internal medicine and pediatric doctors to additionally obtain family doctor qualifications. Practical Implementation Examples Competency Platform Health Care Specialist Competency Platform: An IT tool is planned to be created to monitor and plan the professional development and practical skills acquisition processes of health care specialists. Regional Initiatives Strengthening Regional Health Care Centers: Projects are being carried out in regional health care centers to strengthen the composition and competencies of specialist teams, thereby ensuring better service accessibility.
Dispositions relatives aux filières permettant, après avoir exercé en milieu rural, d’accéder à une nouvelle profession ou de se spécialiser
The Ministry of Health has initiated changes to the Regulations for the Implementation and Supervision of Medical Residency and Dental Residency Programs, as approved by the Government's decree. The changes, effective from January 1, 2023, include extending the duration of certain residency programs and introducing a minimum requirement for professional practice. Specifically, by 2027, at least 35% of medical residents' professional practice must be completed outside university hospitals. To qualify as a residency base, healthcare institutions now only need to have a medical resident mentor (a new role) responsible for overseeing the acquisition of practical skills by medical residents, replacing the previous requirement for a medical resident supervisor. Funds from the initiative will be used to train doctors who wish to become medical resident mentors. Additionally, the Ministry of Health is implementing an EU-funded project titled "Recruiting Specialists to Reduce Health Disparities" (Project No. 08.4.2-ESFA-V-617), with a budget of €668,800. This project aims to fund residency training for doctors (at least 34 individuals) who commit to working for a minimum of 2 years in healthcare facilities in specific districts, as stipulated in their agreements.
Autres
[Q2x2x3x1]
2.2.3.1 Incitations Mesures
Remboursement additionnel
Additional Salary Supplements: Health professionals working in regions or specialties with significant shortages may receive additional salary supplements. These supplements aim to make positions in underserved or high-need areas more attractive. Retention Bonuses: Financial bonuses are offered to healthcare workers who commit to staying in their positions for an extended period, particularly in areas with high demand or difficult working conditions. Financial Support for Education and Training Study Funding: Financial support is provided to cover the costs of education for students pursuing degrees in health-related fields. This can include scholarships or loans that are partially forgiven if the recipient works in designated underserved areas. Training and Certification Costs: Funds are allocated to cover the costs of professional development and certification for existing health care professionals. This includes costs associated with additional qualifications, specialized training, and continuing education. Support for Recruitment and Retention Relocation Assistance: Financial aid is provided to healthcare professionals who relocate to work in high-need areas. This can include relocation expenses, housing allowances, and other support to ease the transition. Employment Grants: Grants or subsidies are offered to health care institutions to support the hiring of additional staff. These funds can help offset the costs associated with expanding services or increasing staff numbers. Incentives for Mentorship and Supervision Mentorship Stipends: Financial incentives are offered to experienced professionals who take on mentorship roles, particularly in training new specialists or supervising their work. This aims to encourage experienced professionals to share their knowledge and support the development of new talent. Supervision Allowances: Additional funding is provided to institutions that facilitate supervision and support for new or less experienced health care professionals. Bonuses for Extra Duties and Responsibilities Performance-Based Bonuses: Health professionals who take on additional duties or responsibilities beyond their standard roles may receive performance-based bonuses. This includes taking on extra shifts, working in challenging conditions, or providing additional services. Specialty Bonuses: Additional financial incentives are given to professionals who acquire specialized skills or work in high-demand specialties, such as emergency medicine, psychiatry, or geriatrics. Implementation and Monitoring Evaluation and Adjustments: The effectiveness of these financial measures is regularly evaluated to ensure they meet their goals of addressing shortages and improving workforce retention. Adjustments are made based on feedback from health professionals and performance data. Transparency and Communication: Clear communication about available financial support and eligibility criteria is essential to ensure that health professionals are aware of the incentives and can access them effectively.
Possibilités de formation
To ensure the occupancy of state-funded study places and to enhance the prestige of certain professional qualifications, as well as to encourage professional orientation and shift public perceptions about specific healthcare professions, the following communication activities are planned: 1. Sharing Professional Experience: Healthcare professionals (preferably from the same cities) will visit schools and high schools to share their professional experiences and career paths. 2. Encouragement Events: Events, practical assignments, and tours of healthcare institutions will be organized to motivate students to choose healthcare professions, providing them with a clearer understanding of the benefits and challenges of these careers. 3. Information Dissemination for Medical Students: Dissemination of information among medical students in integrated studies, guiding them to choose the most needed qualifications after six years of study, such as family medicine, emergency medicine, geriatrics, and psychiatry. 4. Information Dissemination for Nursing Students: Information dissemination and incentives will be targeted at general practice nursing students to better inform them about their career options and opportunities in the healthcare sector. These activities aim to shift societal attitudes towards healthcare professions and encourage young people to pursue careers in this field.
Possibilités de promotion professionnelle ou de développement professionnel
To enhance the competencies of healthcare professionals and other specialists in the healthcare field and ensure continuous professional development, the goal is to provide new knowledge and improve practical skills. This includes integrating advanced healthcare services and working with innovative, cutting-edge technologies. From the 2014-2020 EU funding period and the 2014-2021 European Economic Area Financial Mechanism "Health" program, various projects were implemented to enhance specialists' qualifications. However, due to the ongoing need for continuous improvement to enhance service quality, qualifications development and retraining activities will continue into the 2022-2030 period. Experiences from pandemic management encourage the exploration of solutions to strengthen primary healthcare, expand telemedicine and mobile service options (such as remote consultations, patient monitoring, home visits by family doctors, emotional support, health maintenance advice, etc.). Advances in health technology and the precision of diagnostic and treatment methods are altering the roles of various professions in the treatment process and presenting new challenges for ensuring the safety and quality of health services. This involves planning, evaluating, maintaining, and improving the competencies of healthcare professionals to meet medical standards and creating favorable conditions for implementing innovative healthcare service delivery models. In restructuring the network of healthcare institutions, the aim is to ensure that primary care services within the scope of family medicine are provided exclusively by a fully-fledged family medicine team. This team would include a family doctor, nurses, a midwife, a nursing assistant, a physiotherapist, a lifestyle medicine specialist, and a case manager. The functions of team members should be allocated based on their developed competencies to enhance service quality and accessibility through more effective use of specialist skills. For a fully integrated family medicine team, it is essential to ensure not only a complete composition of required specialists but also the redistribution of their responsibilities, ongoing qualification improvement/retraining (e.g., internal medicine and pediatric specialists could acquire additional qualifications in family medicine), adaptation of existing service delivery methodologies, algorithms, and recommendations, as well as the development and implementation of new ones.
Reconnaissance des compétences professionnelles
Reconnaissance sociale
Public Visibility: The activities of healthcare professionals are often highlighted through media, social networks, and other communication channels. This helps the public learn about their achievements and contributions to the healthcare system. Awards and Recognition Ceremonies: Awards ceremonies are held to honor healthcare professionals who have achieved significant results or contributed to important projects. These awards may be given by the state, municipalities, or professional associations. Patient Feedback: Patient reviews and gratitude letters are also considered important aspects of social recognition. Many healthcare professionals receive positive feedback from patients who value their work and commitment. Professional Organization Recognition: Professional organizations and associations evaluate and acknowledge the contributions and achievements of specialists, granting them certificates, titles, or other recognition markers. Educational and Public Awareness Activities Profession Promotion in Schools and Universities: Events, seminars, and practical tasks are organized in schools and universities where professionals share their experiences with young people. This helps improve the image of the profession and encourages youth to choose a career in healthcare. Public Awareness Campaigns: Organizations and institutions run campaigns to increase public understanding of the work and importance of healthcare professionals. This may include advertising campaigns, social media posts, informational posters, and more. Documentation of Professional Achievements Professional Achievements Documentation: Healthcare professionals can be recognized for their achievements, such as scientific research, innovations, or exceptional services. These achievements can be published in scientific journals, healthcare magazines, or other sources. Social Responsibility Projects: Involvement in social responsibility projects, such as free health screenings, educational programs, or assistance to socially vulnerable groups, also contributes to social recognition. Participation in International Projects International Projects and Collaboration: Participation in international healthcare projects and collaboration with foreign professionals provides opportunities for international recognition and experience, which can enhance social recognition at the national level. Career and Professional Development Career Opportunities: Various career development and professional growth opportunities are provided, including leadership positions, teaching, and mentoring roles, which help professionals gain recognition for their contributions and experience in the healthcare system.
Possibilité d’accès au statut de résident permanent et/ou à la citoyenneté pour les personnels de santé internationaux
Autres
[Q2x2x4x1]
2.2.4.1 Appui Mesures
Conditions de travail sûres et décentes
Health and Safety Regulations Occupational Health and Safety Standards: Lithuania adheres to strict occupational health and safety regulations that apply to all workplaces, including healthcare facilities. These regulations ensure that healthcare professionals work in environments that minimize risks and protect their health. Regular Safety Inspections: Healthcare facilities undergo regular safety inspections to ensure compliance with health and safety standards. This includes checking for proper sanitation, ergonomic workplace design, and adequate safety equipment. Workplace Safety Training Mandatory Training Programs: Healthcare professionals are required to undergo regular training in workplace safety, including emergency procedures, infection control, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Continuing Education: Ongoing education programs are provided to keep healthcare workers informed about the latest safety protocols, technological advancements, and best practices. Supportive Work Environment Ergonomic Workspaces: Facilities are designed to be ergonomic, reducing physical strain and preventing injuries. This includes adjustable furniture, proper lighting, and equipment designed to minimize physical effort. Mental Health Support: Recognizing the high stress associated with healthcare professions, mental health support and counseling services are available to help professionals manage stress and prevent burnout. Infection Control Measures Infection Prevention Protocols: Healthcare settings are equipped with rigorous infection control protocols to protect staff from exposure to harmful pathogens. This includes regular disinfection of surfaces, proper waste management, and protocols for handling infectious materials. Vaccination Programs: Vaccination programs are in place to protect healthcare professionals from infectious diseases. These programs are regularly updated based on current health threats. Fair Compensation and Benefits Competitive Salaries: Efforts are made to ensure that salaries for healthcare professionals are competitive and reflect the high level of responsibility and expertise required. Additional Benefits: Healthcare professionals receive additional benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, and retirement plans, contributing to their overall job satisfaction and security. Work-Life Balance Flexible Scheduling: Initiatives to improve work-life balance include flexible scheduling options and support for part-time work or job-sharing arrangements. Leave Policies: Generous leave policies, including sick leave, parental leave, and vacation time, are in place to help professionals manage their personal and family responsibilities. Emergency Preparedness Preparedness Plans: Healthcare facilities have emergency preparedness plans in place for dealing with crises such as natural disasters, pandemics, or mass casualty events. These plans are regularly reviewed and updated. Crisis Training: Regular crisis management training ensures that healthcare professionals are prepared to handle emergencies effectively and safely. Legal Protections Legal Framework: Lithuanian labor laws provide protections for healthcare professionals, including regulations on working hours, breaks, and conditions of employment. Reporting Mechanisms: There are established mechanisms for reporting unsafe working conditions or occupational hazards, ensuring that concerns are addressed promptly and effectively.
Conditions de vie sûres et décentes
Possibilités d’apprentissage à distance/en ligne
Autres
[Q3x1]
Existe-t-il dans votre pays des politiques et/ou des lois spécifiques qui régissent le recrutement international, les migrations et l’intégration des personnels de santé formés à l’étranger ?
Non
[Q3x2]
Existe-t-il dans votre pays des politiques et/ou des dispositions relatives aux services de télésanté internationaux assurés par des personnels de santé basés à l’étranger ?
Non
[Q3x3]
Votre pays a-t-il constitué une base de données ou une compilation des lois et des réglementations en matière de recrutement et de migrations des personnels de santé internationaux et, le cas échéant, des informations relatives à leur mise en œuvre ?
Non
[Q4]
Considérant le rôle d’autres entités gouvernementales, le Ministère de la santé dispose-t-il de mécanismes (par exemple, des politiques, des processus, une unité) pour assurer le suivi et la coordination entre les secteurs sur les questions liées au recrutement international et aux migrations des personnels de santé ?
Non
[Q5]
Veuillez décrire les mesures prises par votre pays pour mettre en œuvre les recommandations suivantes du Code:
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
5.1 Des mesures ont été prises ou sont envisagées pour modifier les lois ou les politiques relatives aux personnels de santé conformément aux recommandations du Code.
On July 31, 2024, Order No. V-788 was issued, titled “Order on the approval of the procedure for updating the educational competencies of the resident physician supervisor and acquiring and updating the educational competencies of the resident physician mentor.”
5.2 Des mesures ont été prises afin de communiquer et de partager l’information sur le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé d’un secteur à l’autre, ainsi que pour faire connaître le Code aux ministères, départements et organismes concernés, au niveau national et/ou infranational.
On July 5, 2024, at the national and / or regional level, a letter titled “Request to provide information and conduct active communication“ was sent to healthcare institutions. The purpose was to gather information on all agreements established and terminated by healthcare institutions and/or municipalities regarding the employment of specialists under contractual obligations. Additionally, the letter requested information on the incentive measures implemented by healthcare institutions to attract health specialists, as well as details regarding vacant positions for healthcare specialists.
5.3 Des mesures ont été prises pour consulter les parties prenantes lors de la prise de décisions et/ou pour les associer aux activités liées au recrutement international des personnels de santé.
See the previous information provided in section 5.2
5.4 Les autorités compétentes tiennent des registres sur toutes les agences de recrutement privées de personnels de santé autorisés à exercer sur leur territoire.
5.5 Les bonnes pratiques, telles que définies par le Code, sont encouragées et promues auprès des agences de recrutement privées.
5.5a Promotion du Code auprès des agences de recrutement privées.
5.5b Législation ou politique nationale exigeant des pratiques éthiques de la part des agences de recrutement privées, conformément aux principes et aux articles du Code.
5.5c Certification publique ou privée concernant le respect des pratiques éthiques par les agences de recrutement privées.
5.5d Autres
5.6 Aucune des réponses ci-dessus
Government Agreements
[INFOxNRI6]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx3]
Accords entre États relatifs aux migrations ou la mobilité des personnels de santé
[Q6]
Votre pays a-t-il mis en place au niveau national ou infranational des accords et/ou des dispositifs bilatéraux, multilatéraux ou régionaux en matière de recrutement international et/ou de mobilité des personnels de santé ?
Non
Responsibilities, rights and recruitment practices
[INFOxNRI9]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx4]
Responsabilités, droits et pratiques de recrutement
[Q7]
Si votre pays emploie/accueille des personnels de santé internationaux afin qu’ils travaillent dans les secteurs de la santé et de l’aide à la personne, quelles protections juridiques et/ou quels autres mécanismes ont été mis en place pour les personnels de santé migrants et pour veiller à ce qu’ils aient les mêmes droits et les mêmes responsabilités que les personnels de santé formés dans le pays ?
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Les personnels de santé migrants sont recrutés au moyen de mécanismes qui leur permettent d’apprécier les avantages et les risques que présentent les postes à pourvoir et de prendre des décisions éclairées en temps voulu sur ces emplois.
Les personnels de santé migrants sont engagés, promus et rémunérés d’après des critères objectifs tels que les compétences, le nombre d’années d’expérience et les responsabilités professionnelles, sur la même base que les personnels de santé formés dans le pays.
The same conditions and requirements are applied as for Lithuanian health care specialists
Les personnels de santé migrants ont les mêmes opportunités que les personnels de santé formés dans le pays pour améliorer leur formation professionnelle, leurs compétences et la progression de leur carrière.
The same conditions and requirements are applied as for Lithuanian health care specialists
Des dispositions institutionnelles sont en place pour garantir la sécurité des migrations/de la mobilité et l’intégration des personnels de santé migrants.
Des mesures ont été prises pour promouvoir la migration circulaire des personnels de santé internationaux
Autres mesures (y compris juridiques et administratives) visant à établir des pratiques équitables pour le recrutement et l’emploi des personnels de santé formés à l’étranger et/ou immigrés (veuillez préciser)
Aucune mesure n’a été mise en place
Sans objet – N’accueille/n’emploie pas de personnels de santé étrangers
[Q8]
Si des personnels de santé de votre pays travaillent à l’étranger dans les secteurs de la santé et de l’aide à la personne, veuillez indiquer les mesures qui ont été prises ou qui sont prévues dans votre pays pour garantir un recrutement et un emploi équitables, une migration sans danger, leur retour ; et le recours à la diaspora dans votre pays, ainsi que les difficultés rencontrées.
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Veuillez cocher tous les éléments qui s’appliquent dans la liste ci-dessous:
Dispositions pour un recrutement équitable
Dispositions relatives à des contrats de travail décents et à des conditions de travail décentes dans les pays de destination
Dispositions pour une mobilité sans risques
Dispositions pour le retour et la réintégration sur le marché du travail de la santé dans votre pays
Dispositions relatives au recours à la diaspora pour soutenir le système de santé de votre pays
Autres
Aucune mesure n’a été mise en place
The same conditions and requirements are applied as for Lithuanian health care specialists
Sans objet – Les personnels de santé de mon pays ne travaillent pas à l’étranger
International migration
[INFOxNRI10]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx5]
Filières des migrations internationales et de la mobilité des personnels de santé
[Q9x1]
9.1 Si votre pays accueille des personnels de santé internationaux pour travailler dans le secteur de la santé et de l’aide à la personne, comment viennent-ils dans votre pays ? (Cochez toutes les réponses qui s’appliquent)
| Demande directe (individuelle) à des fins d’éducation, d’emploi, de commerce, d’immigration ou d’entrée dans le pays | Accords entre États autorisant la mobilité des personnels de santé | Agences de recrutement privées ou recrutement facilité par l’employeur | Mobilité facilitée par des cabinets de conseil privés spécialisés dans l’éducation/l’immigration | Autres filières (veuillez préciser) | Quelle est la filière la plus utilisée ? Veuillez fournir des données quantitatives si elles sont disponibles. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Médecins | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Personnel infirmier | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Sages-femmes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Dentistes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Pharmaciens | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
[Q9x1oth]
[Q9x2]
9.2 Si des personnels de santé de votre pays travaillent/étudient à l’étranger, comment quittent-ils votre pays ? (Cochez toutes les réponses qui s’appliquent)
| Demande directe (individuelle) à des fins d’éducation, d’emploi, de commerce, d’immigration ou d’entrée dans le pays | Accords entre États autorisant la mobilité des personnels de santé | Agences de recrutement privées ou recrutement facilité par l’employeur | Mobilité facilitée par des cabinets de conseil privés spécialisés dans l’éducation/l’immigration | Autres filières (veuillez préciser) | Quelle est la filière la plus utilisée ? Veuillez fournir des données quantitatives si elles sont disponibles. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Médecins | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Personnel infirmier | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Sages-femmes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Dentistes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Pharmaciens | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Autres métiers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
[Q9x2oth]
Recruitment & migration
[INFOxNRI11]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx6]
Données relatives au recrutement et aux migrations des personnels de santé internationaux
Il est essentiel d’améliorer la disponibilité et la comparabilité internationale des données pour comprendre et gérer les dynamiques mondiales des migrations des agents de santé. Veuillez consulter votre point focal CNPS, le cas échéant, pour vous assurer que les données rapportées ci-dessous sont conformes aux rapports CNPS*.
(Pour plus de détails sur le point focal CNPS de votre pays, veuillez consulter la version électronique de l’INN ou contacter WHOGlobalCode@who.int)
[Q10]
Votre pays dispose-t-il d’un ou de plusieurs mécanismes ou entités chargés de tenir des registres statistiques sur les personnels de santé nés et formés à l’étranger ?
Oui
[Q10x1]
Où les registres sont-ils conservés ? (Cochez toutes les réponses qui s’appliquent)
Relevés d’emploi ou permis de travail
Base de données des personnels du Ministère de la santé
Registre des personnels de santé autorisés à exercer
Autre
[Q10x2]
Le registre comprend-il des données ventilées par sexe sur les personnels de santé nés à l’étranger et/ou formés à l’étranger ?
Oui
Inflow and outflow of health personnel
[INFOxNRI12]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx7]
Entrée et sortie des personnels de santé
[Q11]
Disposez-vous d’un mécanisme de suivi des entrées et sorties des personnels de santé à destination et en provenance de votre pays ? (Cochez toutes les réponses qui s’appliquent)
Entrée
Sortie
Non
[Q11xI]
Si vous avez répondu « Oui » pour « Entrée » :
[Q11x1]
Combien de personnels de santé formés à l’étranger ou nés à l’étranger ont été nouvellement actifs (de manière temporaire et/ou permanente) dans votre pays au cours des trois dernières années (entrée) ?
| Médecins | Personnel infirmier | Sages-femmes | Dentistes | Pharmaciens | Remarques | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 42 | 4 | 3 | 9 | 0 | |
| 2022 | 130 | 51 | 0 | 45 | 3 | |
| 2023 | 92 | 58 | 2 | 32 | 16 | |
| Source des données (p. ex., organisme de réglementation, dossiers d’immigration, permis de travail, etc.) | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses and Compulsory Health Insurance Fund Information System, licenced specialists | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses and Compulsory Health Insurance Fund Information System, licenced specialists | Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses |
[Q11x3]
Si vous disposez d’un document contenant des informations sur les flux d’entrée et de sortie des personnels de santé dans votre pays, veuillez le télécharger.
Stock of health personnel
[INFOxNRI13]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx8]
Stock de personnels de santé
[Q12x1]
Stock consolidé de personnels de santé, ventilé par pays de formation et de naissance
Pour la dernière année disponible, conformément aux indicateurs 1-07 et 1-08 des comptes nationaux des personnels de santé (CNPS), veuillez fournir des informations sur le stock total de personnels de santé dans votre pays (de préférence la main-d’œuvre active), ventilées par lieu de formation (formés à l’étranger) et par lieu de naissance (nés à l’étranger).
Pour la dernière année disponible, conformément aux indicateurs 1-07 et 1-08 des comptes nationaux des personnels de santé (CNPS), veuillez fournir des informations sur le stock total de personnels de santé dans votre pays (de préférence la main-d’œuvre active), ventilées par lieu de formation (formés à l’étranger) et par lieu de naissance (nés à l’étranger).
[Q12x1a]
Veuillez fournir des données sur le stock de personnels de santé actifs dans votre pays par l’un des moyens suivants:
Remplissez le tableau ci-dessous
[Q12x1x1]
| Médecins (généralistes + spécialistes) | 17421 | 17101 | 186 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||
| Personnel infirmier | 26769 | 26492 | 216 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||
| Sages-femmes | 1089 | 1084 | 5 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||
| Dentistes | 4806 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 | ||||||||
| Pharmaciens | 3536 | 3515 | 19 | Hygiene institute and Register of health care and pharmacy practice licenses | 2023 |
[Q12x1x1x]
Si vous disposez d'un document contenant des informations sur le stock de personnels de santé actifs dans votre pays, leur répartition par lieu de formation et par lieu de naissance, veuillez le télécharger.
[Q12x2]
Veuillez fournir des données sur les dix principaux pays où sont formés les personnels de santé étrangers présents dans votre pays.
Ces informations peuvent être fournies par l’un des deux moyens suivants:
Ces informations peuvent être fournies par l’un des deux moyens suivants:
Remplissez le tableau ci-dessous
[Q12x2x1]
| Médecins | Personnel infirmier | Sages-femmes | Dentistes | Pharmaciens | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total des personnels formés à l’étranger | 186 | 216 | 5 | 19 | |
| Pays 1: Pays de formation | UKR | UKR | UKR | UKR | |
| Pays 1: Nombre de personnels | 103 | 103 | 2 | 16 | |
| Pays 2: Pays de formation | RUS | RUS | RUS | RUS | |
| Pays 2: Nombre de personnels | 25 | 35 | 2 | 3 | |
| Pays 3: Pays de formation | BLR | BLR | BLR | ||
| Pays 3: Nombre de personnels | 36 | 38 | 1 | ||
| Pays 4: Pays de formation | EST | POL | |||
| Pays 4: Nombre de personnels | 7 | 15 | |||
| Pays 5: Pays de formation | KAZ | LVA | |||
| Pays 5: Nombre de personnels | 4 | 17 | |||
| Pays 6: Pays de formation | AZE | ||||
| Pays 6: Nombre de personnels | 2 | ||||
| Pays 7: Pays de formation | |||||
| Pays 7: Nombre de personnels | |||||
| Pays 8: Pays de formation | |||||
| Pays 8: Nombre de personnels | |||||
| Pays 9: Pays de formation | |||||
| Pays 9: Nombre de personnels | |||||
| Pays 10: Pays de formation | |||||
| Pays 10: Nombre de personnels | |||||
| Source (par ex. registre professionnel, données de recensement, enquête nationale, autres) | |||||
| Année de collecte des données (Veuillez fournir les données correspondant à la dernière année disponible) | 2023 | 2023 | 2023 | 2023 | |
| Observations |
[Q12x2x1x]
Si vous disposez d’un document contenant des informations sur la répartition des personnels de santé formés à l’étranger dans votre pays en fonction de leur pays de formation, veuillez le télécharger.
Technical and financial support
[INFOxNRI14]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx9]
Appui technique et financier
[Q13]
Votre pays a-t-il fourni une assistance technique ou financière à des pays sources ou à des pays figurant sur la Liste OMS d’appui et de sauvegarde pour les personnels de santé 2023, ou à d’autres pays à revenu faible ou intermédiaire, pour le développement des personnels de santé, le renforcement des systèmes de santé ou la mise en œuvre d’autres recommandations du Code (par exemple, renforcement des données, informations et recherches sur les personnels de santé en vue d’une transposition dans les politiques et la planification, etc.)
Non
[Q14]
Votre pays a-t-il reçu une assistance technique ou financière d’un État Membre de l’OMS ou d’autres parties prenantes (par exemple, partenaires de développement, autres agences) pour le développement des personnels de santé, le renforcement des systèmes de santé ou la mise en œuvre d’autres recommandations du Code (par exemple, renforcement des données, information et recherche sur les personnels de santé en vue de leur transposition dans les politiques et la planification, etc.) ?
Oui
[Q14x]
Veuillez fournir des renseignements supplémentaires ci-dessous (Cochez toutes les réponses qui s’appliquent) :
Appui au développement des personnels de santé (planification, éducation, emploi, fidélisation)
Appui à d’autres éléments de renforcement du système de santé (prestation de services ; systèmes d’information sanitaire ; financement de la santé ; technologies et produits médicaux ; et direction et gouvernance de l’action sanitaire)
Autres domaines d’appui :
[Q14x1]
Appui au développement des personnels de santé (planification, éducation, emploi, fidélisation)
| Pays/entité à l’origine de l’appui | Type d’appui (veuillez préciser) | |
|---|---|---|
| Europe Union | Lithuania has accessed significant financial support from European Union (EU) structural funds for health system strengthening. These funds have been used to improve healthcare infrastructure, enhance the skills of the health workforce, and implement various health reforms aimed at increasing efficiency and quality in the healthcare system. | |
| Nordic Countries | Partnerships with Nordic Countries: Lithuania has engaged in partnerships with Nordic countries, particularly through the Nordic Council of Ministers, for collaborative projects focused on health system strengthening and workforce development. These partnerships often involve sharing best practices, training, and capacity building. | |
| Norway, Sweden and Germany | Lithuania has also received support from various development partners, including bilateral assistance from countries like Norway, Sweden, and Germany. These countries have provided both technical expertise and funding for projects related to health workforce development, including training programs, exchange of knowledge, and implementation of health system reforms. | |
[Q14x2]
Appui à d’autres éléments de renforcement du système de santé (prestation de services ; systèmes d’information sanitaire ; financement de la santé ; technologies et produits médicaux ; et direction et gouvernance de l’action sanitaire)
| Pays/entité à l’origine de l’appui | Type d’appui (veuillez préciser) | |
|---|---|---|
| Europe Union | Technical support was received in the form of COVID-19 tests, vaccines, and other technical tools to facilitate the work of healthcare professionals during the pandemic. | |
Constraints, Solutions, and Complementary Comments
[INFOxNRI15]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[INFOx10]
Obstacles, solutions et observations complémentaires
[Q15]
Veuillez énumérer, par ordre de priorité, les trois principaux obstacles à un recrutement international éthique des personnels de santé dans votre pays et proposer des solutions envisageables :
| Principaux obstacles | Solutions/recommandations envisageables | |
|---|---|---|
| Social Integration and Public Perception | Public Awareness Campaigns: Implement targeted campaigns to promote the benefits of migration and multiculturalism, emphasizing success stories and contributions of migrants. | |
| Policy and Legal Framework | Policy Reform: Update and harmonize migration laws to align with international human rights standards, ensuring that they are flexible enough to respond to evolving migration patterns. International Cooperation: Strengthen bilateral and multilateral agreements with source countries to manage migration flows more effectively and humanely. | |
| Economic Integration | Recognition of Qualifications: Simplify and streamline the process for recognizing foreign qualifications and work experience, allowing migrants to work in their trained professions. Entrepreneurship Support: Provide resources, mentoring, and financial support for migrants interested in starting their own businesses, which can create jobs and stimulate the local economy. |
[Q16]
De quel appui avez-vous besoin pour renforcer l’application du Code?
Appui au renforcement des données et de l’information sur les personnels de santé
1. Enhanced Data Collection Systems Develop Comprehensive Databases: Create or improve national health personnel databases that capture detailed and up-to-date information on the workforce, including demographics, qualifications, and employment status. Implement Standardized Data Collection Tools: Use standardized tools and methods for collecting data across different regions and institutions to ensure consistency and comparability. 2. Data Analysis and Reporting Build Analytical Capacity: Train staff in data analysis techniques to interpret health workforce data effectively, identify trends, and make data-dr,iven decisions. Generate Regular Reports: Produce and disseminate regular reports on health personnel statistics, including workforce distribution, shortages, and migration patterns. 3. Integration with Health Information Systems Link Data Systems: Integrate health personnel data with broader health information systems to provide a comprehensive view of health service delivery and needs. Ensure Interoperability: Ensure that data systems are interoperable with international databases and frameworks to facilitate comparison and coordination. 4. Data Quality and Validation Implement Quality Assurance Measures: Establish procedures for data validation and quality assurance to ensure the accuracy and reliability of health personnel data. Conduct Regular Audits: Perform regular audits of data collection processes and systems to identify and address issues affecting data quality. 5. Capacity Building and Training Train Data Collectors and Analysts: Provide training for personnel involved in data collection and analysis to enhance their skills and understanding of best practices. Develop Data Management Skills: Offer courses and workshops on data management, including the use of advanced data analysis tools and techniques. 6. Access to Technology and Tools Provide IT Infrastructure: Ensure that health institutions have access to the necessary IT infrastructure and software for effective data collection and management. Support Innovative Solutions: Encourage the adoption of innovative technologies such as mobile data collection apps and cloud-based systems to streamline data processes. 7. Collaboration and Partnerships Engage with International Organizations: Collaborate with international organizations and agencies to access best practices, benchmarks, and support for data initiatives. Foster Interinstitutional Cooperation: Promote cooperation between different institutions and agencies involved in health workforce data collection and management. 8. Public Awareness and Transparency Share Data Publicly: Increase transparency by making health workforce data publicly available, where appropriate, to support accountability and informed decision-making. Promote Data Literacy: Raise awareness about the importance of data and its role in improving health systems, and encourage stakeholders to use data in planning and policy development. 9. Policy and Regulatory Support Establish Data Governance Policies: Develop and implement policies for data governance, including data privacy, security, and ethical considerations. Create Data Standards: Define and enforce standards for data collection, reporting, and analysis to ensure consistency and quality.
Appui au dialogue politique et à l’élaboration des politiques
Appui à l’élaboration d’accords bilatéraux/multilatéraux
Autres
Pas d’appui requis
[Q17]
Étant donné que le Code est un document dynamique qui doit être mis à jour si nécessaire, veuillez nous faire part des réflexions de votre pays sur les 14 années écoulées depuis la résolution sur le Code.
[Q17x1]
Veuillez préciser Le Code est-il utile pour votre pays et, si oui, en quoi ?
Evolving Policy and Regulatory Framework
Adoption and Integration:
Since the adoption of the Code in 2010, Lithuania has progressively integrated its principles into national policies. This has involved aligning local regulations with the Code’s recommendations to ensure ethical recruitment practices and prevent the migration of health personnel from low-resource settings.
Regulatory Updates:
The legal framework has been periodically updated to better align with the Code’s recommendations. This includes regulations governing international recruitment, professional standards, and measures to avoid practices that could negatively impact developing countries.
Enhancing Domestic Workforce Capacity
Training and Education:
Efforts have been made to improve the education and training of domestic health personnel to reduce dependency on international recruitment. This includes expanding medical education opportunities and increasing the capacity of training institutions.
Professional Development:
Continuous professional development programs have been established to ensure that health personnel are equipped with the latest skills and knowledge, thus enhancing the quality of care and reducing the need for international recruitment.
Ethical Recruitment Practices
Monitoring and Compliance:
The country has implemented mechanisms to monitor compliance with ethical recruitment practices. This involves ensuring that recruitment agencies and employers adhere to standards that prevent the exploitation of health personnel from developing countries.
International Collaboration:
Lithuania has engaged in international cooperation to share best practices and collaborate on initiatives that support the Code’s objectives. This includes working with global health organizations and participating in international forums.
Addressing Domestic Needs and Retention
Incentives and Retention Strategies:
To address shortages and retain domestic health personnel, various incentives have been introduced, such as financial benefits, career development opportunities, and improved working conditions.
Public Awareness and Recognition:
Efforts to enhance the social recognition of health professions and promote career paths in healthcare have been undertaken. This includes public campaigns to highlight the value of health workers and their contributions to society.
Evaluating Impact and Adjusting Strategies
Regular Review and Feedback:
The impact of the Code’s implementation has been regularly reviewed through feedback mechanisms, including surveys and evaluations of recruitment practices and workforce conditions. This has helped to identify areas for improvement and adjust strategies accordingly.
Adaptation to Emerging Challenges:
The dynamic nature of the Code has necessitated periodic adjustments to national policies and strategies to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the global health workforce landscape.
[Q17x2]
Y a-t-il des articles du Code qui doivent être mis à jour ?
Non
[Q17x3]
Le processus de production de rapports sur la mise en œuvre du Code et l’examen de la pertinence et de l’efficacité du Code doivent-ils être mis à jour ?
Non
[Q17x4]
Veuillez formuler des commentaires sur la Liste OMS d’appui et de sauvegarde pour les personnels de santé (par ex., si votre pays est inclus dans la liste, en quoi cela vous a-t-il affecté ; si votre pays fait appel à des personnels de santé internationaux, comment la liste vous a-t-elle affecté ; si votre pays n’est pas dans la liste, comment cela vous a-t-il affecté)
[Q18]
Veuillez communiquer toute autre observation ou tout document complémentaire que vous souhaiteriez fournir concernant le recrutement international et les migrations des personnels de santé, dans le cadre de la mise en œuvre du Code.
Veuillez expliquer OU télécharger un document (taille maximale du fichier 10 Mo)
Veuillez expliquer OU télécharger un document (taille maximale du fichier 10 Mo)
[Q18x1]
Warning
[INFOxNRI16]
Instrument national de notification 2024
[WARN]
Vous avez atteint la fin du National Reporting Instrument - 2024. Vous pouvez revenir à n'importe quelle question pour mettre à jour vos réponses ou confirmer votre saisie en cliquant sur « Soumettre ».
